Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-29 Origin: Site








Application And Research of Infrared Heating in Plastic Welding Technology
With the continuous advancement of automotive technology, people's demand for automotive dashboards has also extended from conventional functions to safety, reliability, comfort and many other aspects of human/vehicle interface.Complexity makes the design of the dashboard more and more fanciful; With the increasing proportion of engineering plastics in the automotive field, it is particularly important to choose the appropriate welding method to realize the connection between plastic parts. The limitations of traditional welding processes put forward many requirements for the design itself, which seriously limits the freedom of product design.
Infrared heating technology is suitable for welding parts with complex curved surfaces and large structural plastic parts, which can melt thermoplastics without touching the product through infrared light.The weld between the two parts after welding can reach 100% airtightness, and there will be no welding slag or flash at the weld, etc., and its unique advantages are more and more popular with many automobile manufacturers, and are used in many models today, such as SAIC Volkswagen's Lingdu and Octavia models, Volvo XC60 models, etc.
1 Principle of infrared welding technology
1.1 Introduction to infrared rays
Infrared is one of the many invisible rays in the sun's rays, which is an electromagnetic wave with a wavelength between microwave and visible light, with a wavelength between 1mm and 760nm, and is divided into three regions: short wave (0.75 ~ 1.50 μm), medium wave (1.50 ~ 3.0 μm) and long wave (3.0 ~ 1000 μm), as shown in Figure 1.

1.2 Infrared heating principle
The infrared frequency is low, and it can only penetrate the gaps of atoms and molecules of matter, so that the vibration of atoms and molecules is accelerated and the spacing is widened, thereby increasing the energy of thermal motion. From a macroscopic point of view, matter is melted and vaporized by heat, but the essence of matter does not change, which is the principle of infrared heating.
1.3 Infrared welding
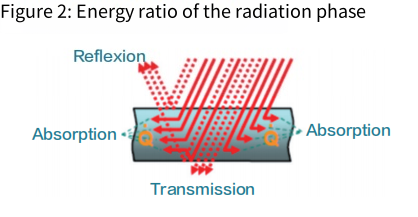
Infrared welding uses a non-contact, radiant heating method to weld plastic parts through an energy-controlled infrared generator. Infrared irradiation occurs on the heated part to reflect, absorb and transmit three conduction modes (as shown in Figure 2), and the part melts the material for welding by absorbing infrared radiated heat to a certain temperature.
When the product is welded by infrared, the infrared generator is inserted between the two plastic parts, and when the workpiece is close to the infrared generator, the part begins to melt. After reaching the pre-set heating time, the weld bar is fully melted, at this time the infrared generator is quickly evacuated, and then the left and right workpieces are merged together, and when a certain welding time and welding depth are reached, the welding process is completed.
The specific welding process is shown in Figure 3: (1) Insert the parts and infrared generator into the designated heating position; (2) Heating to make the welding bar molten; (3) The tire mold is retracted, and the infrared generator returns to the initial position; (4) Mold closing, welding and cooling; (5) Open the tire mold and take out the parts.

2 Infrared generator
2.1 Introduction to Infrared Generator
At present, the infrared welding process has been widely used in the manufacturing of dashboard products. The IR welding tool consists of three parts: the upper tool/or left, the IR generator and the bottom
For tyre / or right tyre (as shown in Figure 4), the infrared generator is the core component. As mentioned earlier, infrared rays are divided into short-wave, medium-wave and long-wave, and each region has its own characteristics: short-wave, strong penetration, and can be absorbed by the material internally; medium wave, the penetration is shallow, and most of it is absorbed by the surface of the material; Long wave, large
It is partially reflected, and a very small amount is absorbed by the surface layer of the substance. Therefore, there are two main forms of infrared generators used in instrument panel manufacturing: quartz glass lamps (short wave) and metal foil (medium wave), as shown in Figure 5.


2.1.1 Quartz glass lamp
Quartz glass lamps consist of quartz glass tubes with a tungsten wire jacket and a reflective layer. Quartz glass tubes have extremely strong infrared transmittance and can be continuously and stably above 1000°C
and has good corrosion resistance. At the same time, in order to better gather the radiation energy of the generator on the heated material, a gold-plated reflective coating will be added to the outer wall of the quartz tube, which can direct more than 90% of the infrared light to improve the infrared heating efficiency.
Quartz glass lamps are divided into standard tubes and special-shaped tubes. Standard tubes are further divided into double tubes and single tubes, as shown in Figure 6.
2.1.2 Metal foil
The foil generator consists of a ceramic mold and a sheet of nickel metal embedded in a groove in the ceramic mold, as shown in Figure 7.
The thermal insulation of the ceramic mold can effectively block the heat radiation effect between the heaters, thereby ensuring the uniformity of product heating; Ceramics can achieve better conformity to ensure consistent heating distances throughout the entire area of the product. Nickel metal sheets are often bent to facilitate installation and fixation in ceramic molds.


Compared with the commonly used quartz glass heating lamp, the effective radiation power of the metal foil generator is more matched with the absorption rate of the material, and the energy utilization efficiency is also higher. Due to the spokes.
The energy level density of the radiation is much lower than that of infrared heating lamps, which also greatly reduces the risk of deformation of plastic parts caused by over-baking.
2.2 Infrared generator selection
The surface temperature of the shortwave generator can reach 1800~2200°C, which can be used for welding plastic parts. Due to low absorption, heat
The radiation penetrates deeper into the material, ensuring uniform heating. At the same time, using a shortwave generator, the speed of reaching the decomposition temperature of the material surface will be slower, so as to avoid thermal damage. The surface temperature of the medium wave generator is between 800~950°C, because most of the heat radiation is absorbed by the most surface material, so the medium wave generation is mainly used to heat the surface material, such as the welding of plastic film and the drying of paint.
Therefore, it is very necessary to choose the right infrared generator for different materials and different process methods. The choice of generator wavelength should be consistent with the absorption spectrum of the material, which
This will allow the product to be heated faster without any additional environmental or equipment heating. Choosing the right infrared generator can greatly reduce the energy consumption of equipment in the factory.
3 Research on the uneven appearance of infrared welding products
In the process of infrared welding, the parts will go through the process of high temperature and gradual cooling, due to the difference in materials, size, characteristic structure and many other factors of the two parts, it will lead to the inconsistency of its cooling speed and shrinkage and deformation degree, and the welding of the product will produce uneven appearance problems due to the existence of internal stress. In addition, the unreasonable parameter setting of the infrared welding process, as well as the structural design defects of infrared welding equipment and molds, will also affect the appearance of the parts. The dashboard of a certain model (skeleton wall thickness 2.5 mm) is connected to the air duct skeleton by infrared welding (infrared heating lamp generator) (as shown in Figure 8), and after welding, it shows different degrees of bulge in the airbag area, which is obvious to the touch.

Infrared welding is a relatively mature plastic welding process in China, which has been used in many model projects, and there has been no feedback on similar obvious bulging defects before. for
To study the cause of the defect, we selected the instrument panel part A with a good appearance of the front foam and the part B with obvious unevenness as the research objects. The remaining factors of the two parts: material grade, skeleton wall thickness, weld shape/quantity, etc. are all the same.
4 Conclusion
The surface temperature of the infrared generator can reach 800~2200°C when working, and the parts will absorb a lot of heat when welded by infrared. Due to the influence of many factors during the cooling process
It leads to the asynchronous cooling speed and deformation, resulting in the generation of internal stress and the occurrence of uneven surface of the product. In actual production, we can start from two aspects: first, from the product structure design, increase the wall thickness of the part, and use the reinforcement-to-reinforcement welding method to improve the deformation resistance of the part itself; Secondly, it can start from reducing the heat absorbed by the parts during the welding process, reducing the welding time, and appropriately reducing the power of the heating tube. Through the combination and complementarity of the two methods, we can obtain more satisfaction
The appearance of the product.

