Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-24 Origin: Site








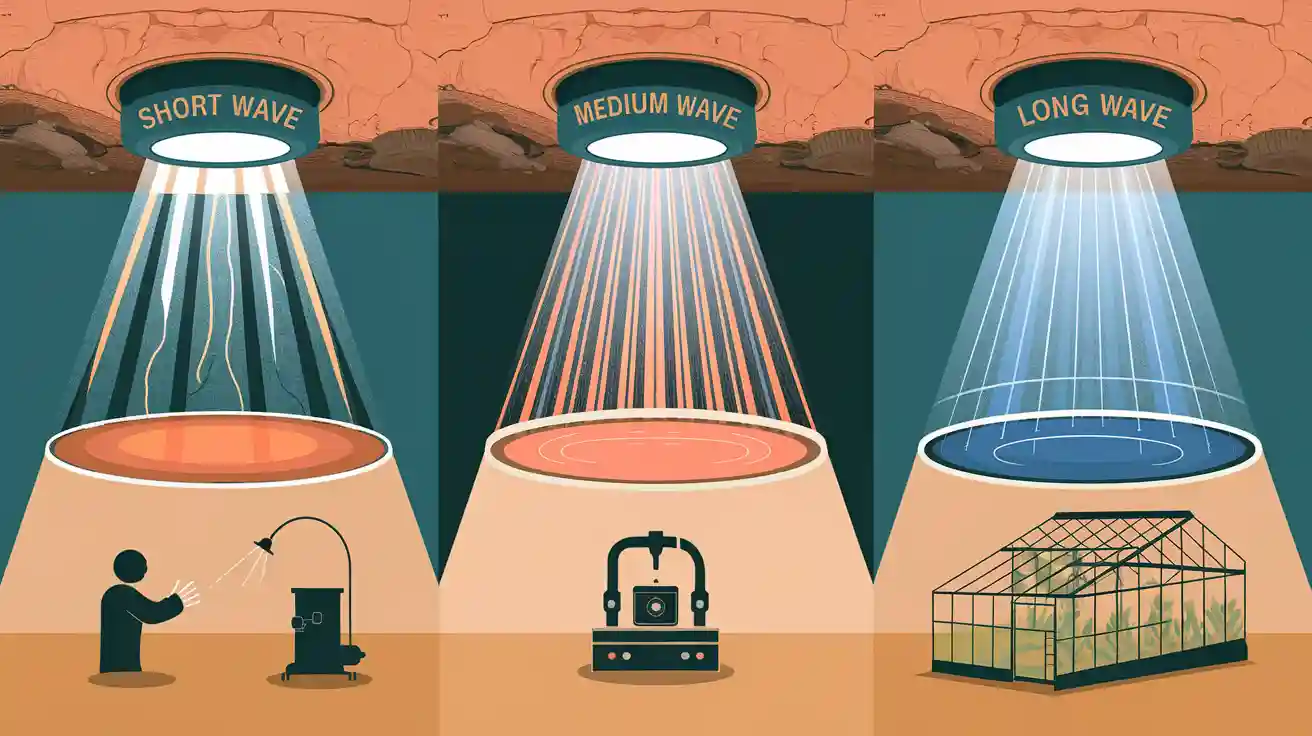
Selecting the right IR tubes depends on the specific heating application. Short wave IR tubes deliver intense heat ideal for industrial processes like metal treatment, while medium and long wave IR tubes suit drying, comfort heating, and applications needing lower temperatures. The table below highlights these differences:
IR Type | Wavelength Range (microns) | Temperature Range | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
Short Wave IR | 0.76 – 2.0 | Up to 5000°F | High-intensity industrial heating |
Medium Wave IR | 1.4 – 3.0 | Up to 1750°F | Drying, plastics, glass, textiles |
Long Wave IR | Above 3.0 | 100–500°C | Comfort and space heating |
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology provides advanced infrared heating solutions, including Quartz IR Emitters, ensuring optimal performance for diverse infrared heating needs.
Short, medium, and long wave IR tubes each provide unique heat suited for different applications, from intense industrial heating to gentle comfort warming.
Short wave IR tubes deliver rapid, high-intensity heat ideal for metal treatment and fast industrial processes, saving energy and space.
Medium wave IR tubes offer balanced heating with good energy efficiency, perfect for plastics, glass, and controlled drying tasks.
Long wave IR tubes produce gentle, uniform heat that suits comfort heating and delicate industrial uses, improving energy savings and comfort.
Matching the IR tube wavelength to the material's absorption improves heating efficiency, product quality, and reduces energy waste.
Infrared heating transfers heat directly to objects, avoiding air heating and improving energy use and indoor air quality.
Proper installation, maintenance, and safety practices extend IR tube life and ensure reliable, safe operation.
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology provides advanced IR tube products and expert support to help users select the best heating solutions.
IR tubes play a vital role in modern heating applications. These devices, often called infrared tubes or lamps, emit infrared energy to deliver targeted heat. Industrial standards, such as those from the USPTO CPC classification, group IR tubes under the broader category of lamps. This classification includes tubes that emit infrared light for various uses. Although no separate industrial standard exists for IR tubes alone, standards like IEC 60240 outline the characteristics of electric infrared emitters for industrial heating.
Manufacturers design IR tubes to meet the demands of many industries. For example, Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology produces Quartz IR Emitters that serve as reliable sources of radiant heat. These products support processes in agriculture, digital printing, glass production, and more. The versatility of IR tubes makes them essential for both industrial and commercial heating solutions.
Note: IR tubes come in different types, such as short wave, medium wave, and long wave, each suited for specific heating requirements.
IR tubes generate infrared radiation through a precise process. Each tube contains a quartz glass enclosure that houses a filament made from materials like tungsten wire or iron-chromium-aluminum alloy. Manufacturers fill the tube with inert gases, such as nitrogen or argon, to protect the filament and enhance efficiency. When electrical current passes through the filament, it heats up rapidly. This process causes the filament to emit infrared energy, which the quartz tube transmits to the surrounding area.
The quartz tube allows most of the radiant energy to pass through, while some energy is absorbed and re-emitted as far infrared rays.
The temperature of the filament determines the wavelength and intensity of the emitted infrared radiation.
As the filament temperature rises, the amount of infrared energy increases, and the peak wavelength shifts to shorter values, following Planck's Law.
At very high temperatures, the filament may also emit visible light, starting as a faint red glow.
Different IR tubes operate at various temperatures and emit specific infrared wavelengths. For instance, quartz tungsten IR tubes can reach up to 2600°C, producing short wave infrared suitable for high-intensity heating. Gas-fired radiant tube heaters use fuel combustion to heat a steel emitter tube, which then radiates infrared energy. The efficiency and effectiveness of each IR tube depend on the materials used and the operating temperature.
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology’s Quartz IR Emitters exemplify advanced electric infrared heating. These products convert electrical energy into infrared radiation with high efficiency, making them ideal for precise and energy-saving heating applications.

Short-wave infrared heating, also known as IR-A or near-infrared, operates in the wavelength range of approximately 0.76 to 2 microns. Most shortwave infrared heaters use tungsten filaments enclosed in quartz glass tubes, often filled with halogen gas. These high-temperature short-wave IR heaters reach filament temperatures between 1800°C and 2400°C, producing intense radiant energy and visible light. The peak emission for a shortwave infrared heater typically falls between 0.75 and 1.4 microns. This range enables rapid and efficient heating, making shortwave IR tubes ideal for applications that demand immediate heat delivery.
Shortwave IR tubes deliver several advantages in heating applications:
Rapid warming: Shortwave infrared heaters provide instant heat to surfaces and people without preheating the air.
Zone-specific control: Operators can target specific areas, optimizing energy use and reducing waste.
Easy installation: These heaters require minimal construction work, preserving flexibility in interior layouts.
Environmentally friendly: Shortwave IR tubes produce no harmful emissions and can operate with CO2-neutral power sources.
High heat output efficiency: Compared to other devices, shortwave infrared heaters deliver up to 2.87 times more warmth for the same power input.
Cost efficiency: Although the initial investment may be higher, energy savings can offset costs within two heating seasons.
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology offers advanced shortwave IR solutions, such as their Short Wave Infrared Lamps and Short Wave Automotive Infrared Heat Lamps. These products excel in industrial drying, metal treatment, and outdoor heating, where rapid and powerful heat is essential.
Medium-wave infrared heating, often called mediumwave or IR-B, emits radiation primarily in the 2 to 15 micron range. Mediumwave IR tubes use quartz glass enclosures and filaments designed for moderate temperatures. The largest emission proportion occurs in the mid-wave IR region, which aligns well with the absorption characteristics of many materials. Mediumwave IR tubes also emit some visible light, but this does not contribute to heating.
Mediumwave IR tubes offer a balanced performance profile:
Radiant efficiency: Mediumwave quartz tubes achieve approximately 60% radiant efficiency.
Heat-up and cool-down rate: These heaters provide medium-speed response, suitable for processes that require controlled heating cycles.
Mechanical ruggedness: Mediumwave IR tubes feature robust construction, ensuring durability in demanding environments.
Moisture resistance: High resistance to moisture makes them suitable for industrial and commercial settings.
Flexible operation: Mediumwave IR tubes support a wide wattage range (450–5200 Watts) and voltage range (120–480 Volts).
Long life expectancy: Flat panel mediumwave emitters can last up to 25,000 hours.
Process control: Optional accessories enhance process control and adaptability.
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology’s Fast Medium Wave Infrared Lamps and Medium Wave Quartz Infrared Heater Lamps exemplify these features. Their products serve industries such as plastics, glass, textiles, and digital printing, where precise and efficient heating is critical.
Long-wave infrared, also known as longwave or far-infrared, covers wavelengths from 8 to 14 microns. Longwave IR tubes operate in the thermal infrared region, where most objects at room temperature emit their infrared radiation. This range is especially sensitive to temperature variations, making longwave IR tubes suitable for comfort heating and thermal imaging.
Longwave IR tubes provide unique benefits for industrial and commercial heating:
Efficient radiant heat: Longwave IR tubes emit primarily in the 3–10 micron range, matching the absorption characteristics of many organic materials and surfaces.
Construction: Most longwave IR tubes use ceramic elements with FeCrAl resistance coils embedded in highly emissive ceramic bodies.
Versatility: Available in various standard sizes, with flat or curved emitting surfaces to suit different applications.
Industrial suitability: Common uses include thermoforming acrylic sheets, curing foam, and preheating carbon fiber fabric.
High efficiency: Some longwave IR tube heaters convert up to 50% of gas input into usable radiant energy, outperforming conventional heaters.
Direct heating: Radiant heat warms objects and people directly, improving comfort and reducing energy consumption.
Durability: Longwave IR tubes feature durable construction with no moving parts, ensuring low maintenance and long service life.
Environmental resistance: Certain models offer corrosion and moisture resistance, ideal for harsh industrial environments.
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology’s Carbon Infrared Lamps and Round Tube IR Lamps for Heating provide reliable longwave IR solutions. These heaters excel in large-scale industrial heating, comfort heating, and applications requiring gentle, even heat distribution.
Tip: Matching the IR tube type to the material and application ensures optimal heating performance and energy efficiency.
Infrared tubes deliver heat through radiant energy, transferring warmth directly to objects and surfaces without relying on air movement. The effectiveness of this heat transfer depends on the wavelength of the infrared energy and the absorption characteristics of the target material.
Shortwave IR tubes operate at extremely high temperatures, producing intense heat and visible light. These tubes excel in industrial environments where rapid, powerful heat is necessary. However, human skin absorbs less of this energy, making shortwave IR less suitable for comfort heating.
Mediumwave IR tubes function at moderate temperatures and emit energy that aligns well with the absorption properties of many materials, including plastics and human skin. This match results in higher heat transfer efficiency and safer, more comfortable heating for both industrial and commercial applications.
Longwave IR tubes work at lower temperatures and emit energy that human skin and organic materials absorb efficiently. This property makes longwave IR tubes ideal for comfort heating and applications requiring gentle, uniform heat.
The efficiency of heat transfer increases when the infrared wavelength matches the absorption peak of the material. For example, mediumwave IR at around 3.45 microns achieves nearly 100% absorption in polypropylene sheets, demonstrating the importance of wavelength selection for efficient heating. Uniform heating across surfaces ensures consistent product quality and process reliability.
Energy efficiency remains a critical factor in selecting an infrared heating solution. Shortwave IR tubes convert a high percentage of electrical energy into radiant heat, often reaching up to 96% efficiency in advanced products like those from Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology. This high conversion rate reduces operational costs and supports sustainable manufacturing.
Mediumwave IR tubes also offer impressive energy efficiency, especially when matched to materials that absorb their specific wavelengths. These tubes provide uniform heating with minimal energy loss, making them suitable for processes that demand precise temperature control and consistent results.
Longwave IR tubes, while operating at lower temperatures, deliver efficient heating for comfort and space applications. Their energy output targets surfaces and people directly, minimizing waste and maximizing comfort. Uniform heat distribution further enhances energy savings by reducing the need for additional heating sources.
Note: Selecting the right infrared tube type for the application ensures optimal energy efficiency and uniform heating, leading to lower energy consumption and improved process outcomes.
The response time of an infrared tube impacts process control and operational flexibility. Shortwave quartz halogen and tungsten infrared emitters feature extremely rapid warm-up and cool-down times, often reaching full heat output within seconds. This quick response allows operators to start and stop heating cycles instantly, which proves valuable in automated production lines or when conveyor belts pause.
Mediumwave and longwave IR tubes, such as quartz cassette and ceramic emitters, generally require longer warm-up and cool-down periods. Although these tubes do not match the speed of shortwave emitters, they still provide reliable and consistent heat for applications where immediate response is less critical. The gradual temperature change supports uniform heating and reduces thermal shock to sensitive materials.
Uniform heat delivery and fast response times contribute to efficient heating processes, improved product quality, and reduced downtime. Operators benefit from precise control over energy input and heat output, optimizing both performance and cost.
Industrial environments demand reliable and efficient heating solutions. Infrared heaters play a crucial role in processes such as metal treatment, glass manufacturing, paint drying, and digital printing. Each IR tube type offers unique advantages for specific industrial applications. The table below summarizes common uses and the effectiveness of each IR tube type:
IR Tube Type | Common Industrial Applications | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
Short-wave IR | Metal industries (e.g., steel mills) for temperature measurement | Delivers accurate temperature data, less sensitive to surface variations and alloys. |
Mid-wave IR | Power plants (coal-burning) to detect slag buildup inside furnace tubes | Detects slag buildup through flames, improving operational efficiency and preventing equipment damage. |
Long-wave IR | Outdoor monitoring (substations, power lines) | Provides reliable temperature monitoring, unaffected by smoke, steam, or solar reflections. |
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology supplies Quartz IR Emitters that meet the rigorous demands of these industries. Their infrared tube heater for garage ensure precise heat control, rapid response, and energy efficiency, supporting applications for medium-wave IR heating such as plastics processing and textile drying. Industries benefit from improved product quality and reduced operational costs.
Infrared heaters have become increasingly popular in commercial and residential settings. These heaters provide targeted heat, warming people and objects directly rather than the air. This approach results in significant energy savings and enhanced comfort. Users report annual fuel cost reductions of 30% to 70% compared to traditional forced air systems. The following list highlights the main benefits of infrared heating in these environments:
Heaters emit low harmful emissions, supporting cleaner indoor air.
Thermal comfort improves as floors and objects receive direct heat, reducing air stratification.
Minimal air movement helps maintain indoor air quality by limiting the spread of pollutants.
Flexible placement and modular design allow for zone control and personalized comfort.
Durable construction and low maintenance requirements ensure long service life.
Fast heat recovery and compatibility with smart controls increase efficiency.
Suitable for a wide range of applications, including commercial, industrial, agricultural, and residential spaces.
The demand for energy-efficient heating continues to grow in the residential sector. Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology’s products deliver reliable performance, making them a preferred choice for engineers and contractors seeking cost-effective solutions.
Outdoor and special heating applications present unique challenges. Heaters must withstand harsh conditions, including wind, moisture, and contaminants. Uniform and comfortable heat distribution remains essential for these environments. Electric infrared heaters with quartz or tubular elements excel in outdoor use, especially when equipped with moisture-resistant terminal housings. These heaters offer high operating temperatures, rapid heat-up and cool-down cycles, and corrosion resistance.
Tip: For patios, garages, and agricultural spaces, choose heaters designed for durability and weather resistance.
Manufacturers design models like the IP67 ULG Ultra Low Glare Infrared Lamps from Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology to perform reliably in outdoor and demanding environments. Their heaters provide clean, efficient heat with minimal loss, easy installation, and compatibility with local power supplies. These features make them ideal for outdoor patios, greenhouses, and special industrial installations where gas heating is impractical.
Infrared heating plays a significant role in metal processing industries. Short-wave IR tubes deliver the high-intensity heat required for metal treatment, forging, and annealing. These tubes reach extremely high temperatures, making them suitable for heating metals with high thermal conductivity and reflectivity. Operators often choose short-wave IR for processes such as preheating, drying coatings, and curing metal surfaces. The rapid response of these tubes allows precise control over heating cycles, which is essential for maintaining product quality.
Medium-wave IR tubes also find use in metal applications, especially when the process requires moderate temperatures. These tubes provide more controlled and uniform heating, which benefits tasks like powder coating and paint drying on metal surfaces. Long-wave IR tubes, while less common in heavy metal processing, can support applications that involve surface finishing or gentle warming of metal components.
Tip: Matching the IR wavelength to the metal’s absorption characteristics improves heating efficiency and reduces energy waste.
Plastics respond well to infrared heating, especially when the IR wavelength aligns with the absorption properties of the specific polymer. Medium-wave IR tubes often provide the best results for plastics, as many polymers absorb energy efficiently in this range. This absorption leads to rapid and uniform heating, which is critical for processes like thermoforming, welding, and drying.
Manufacturers have developed advanced IR heating modules that optimize plastic processing. For example:
Insul-Watt heating modules combine IR elements with ceramic-fiber insulation and vacuum cooling to heat plastics processing barrels quickly and efficiently.
IR elements reach operating temperatures of about 1100°F within 15 seconds, demonstrating fast heating capability.
These systems achieve approximately 90% energy efficiency, much higher than conventional heaters, resulting in about 50% overall energy savings.
Heat distribution remains uniform and consistent, reducing hot and cold spots in the barrel.
The modules cover the entire barrel surface, unlike standard heater bands, which improves heating uniformity.
Closed-loop controls maintain barrel temperature variation within 1°F, ensuring precise temperature management.
The system supports various plastics processing methods, including injection molding, blow molding, extrusion, and compounding.
Although specific plastic types are not detailed, these results show that IR tube heating works effectively for a wide range of plastics processing applications. The ability to deliver fast, uniform, and energy-efficient heat makes IR tubes a preferred choice in the plastics industry.
Glass manufacturing and processing require precise and consistent heating. Infrared tubes, especially medium-wave and short-wave types, excel in this field. Medium-wave IR tubes match the absorption characteristics of glass, allowing for even heating during forming, bending, and tempering. Short-wave IR tubes provide the intense heat needed for rapid processing or when working with thicker glass sections.
Operators use IR heating for tasks such as preheating, edge sealing, and laminating glass panels. The direct radiant heat minimizes thermal shock and reduces the risk of cracking. Uniform heat distribution ensures high-quality finished products with fewer defects. Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology’s Quartz IR Emitters offer reliable solutions for glass heating, supporting both high-speed production and delicate processing tasks.
Heating organic materials with infrared (IR) technology requires careful selection of both the infrared tube type and the construction materials of the heater. Organic substances, such as food, textiles, paper, and certain polymers, respond differently to various IR wavelengths and heating characteristics. The choice of IR tube impacts not only the efficiency of heat transfer but also the durability and safety of the heating process.
Quartz IR emitters stand out as the preferred solution for rapid and intense heating of organic materials. These tubes reach high operating temperatures—up to 1600°F—and deliver short-to-medium wavelength infrared energy. This capability enables fast surface heating, which proves essential in applications like food processing, drying of agricultural products, and rapid curing of coatings on organic substrates. Studies by Krishnamurthy et al. (2008) and Janani Srinivasan (2020) demonstrate that quartz and halogen IR tubes improve food quality by inducing Maillard reactions and protein denaturation. These reactions enhance flavor, texture, and microbial safety in processed foods. The quick warm-up time of quartz tubes also supports high-throughput industrial operations.
Ceramic IR heaters offer a cost-effective alternative for broader, less intense heating needs. These heaters emit medium-wavelength infrared energy and require a longer warm-up period—up to five minutes. Their design makes them suitable for air heating around organic materials, such as in drying rooms for textiles or paper. Ceramic heaters provide even heat distribution and easy replacement, making them a practical choice for many commercial applications.
Metal-sheathed IR heaters excel in environments where durability and corrosion resistance are critical. Manufacturers often use titanium-stabilized or stainless steel for these tubes, ensuring performance in harsh or humid conditions. Metal-sheathed heaters can reach temperatures up to 2000°F and are ideal for heating organic liquids or operating in rugged industrial settings. Their robust construction allows for submerged heating and long service life.
IR Tube Heater Type | Heating Characteristics | Recommended Use for Organic Materials | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
Quartz | Rapid heat-up, short-to-medium wavelength, high temperature (up to 1600°F) | Best for high-heat, fast heating of plastics, food, and other organic substances | Instantaneous heating, small size, high operating temperature |
Ceramic | Slower heat-up (up to 5 minutes), broad heating, medium wavelength | Affordable option for broad heating needs, suitable for air heating around organic materials | Cost-effective, easy replacement |
Metal-Sheathed | Durable, slower heat-up, can reach up to 2000°F, corrosion resistant with coatings | Ideal for heating liquids, corrosive substances, and rugged environments involving organic materials | High durability, corrosion resistance, suitable for submerged heating |
Tip: Selecting heater radiant tube made from titanium-stabilized or stainless steel enhances corrosion resistance and heat tolerance, especially in humid or chemically aggressive environments.
Infrared heating of organic materials offers significant benefits, including energy efficiency, improved product quality, and process flexibility. Quartz IR emitters from Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology deliver the rapid, targeted heat required for demanding industrial applications. Ceramic and metal-sheathed options provide versatility for broader or more challenging environments. By matching the IR tube type and construction material to the specific needs of the organic material, operators achieve optimal heating performance and long-term reliability.
Short wave IR tubes offer a range of advantages that make them highly effective for demanding heating applications. The table below summarizes their key strengths:
Advantage Category | Description |
|---|---|
Rapid Heating Speed | Energy is absorbed directly by material molecules, resulting in extremely fast temperature rise. |
Surface and Partial Penetration Heating | Heats surfaces quickly and penetrates to some depth, preserving material properties. |
Selective Wavelength Matching | Allows precise matching to material absorption bands, optimizing efficiency and quality. |
Energy Saving | Consumes less energy than traditional electric or fuel-based methods. |
Environmental Benefits | Emits no exhaust gases, supporting eco-friendly operations. |
Customizable Design | Can be tailored in shape, size, power, and wavelength for specific needs. |
Fast and Efficient | High energy density and wavelength selectivity improve product quality. |
Space Saving | Occupies less space than conventional hot air furnaces. |
Easy Control | Intelligent systems enable precise temperature regulation and quick response. |
Short wave IR tubes deliver instant heat without preheating, leading to significant energy savings. They provide rapid and uniform heating, eliminate cold spots, and do not rely on air circulation. These features improve indoor air quality and allow zone heating, which reduces overall expenses. Their compact design enables easy installation, and their operation remains safe with no open flames or harmful emissions.
Despite their many benefits, short wave IR tubes present some limitations:
Higher dark current in sensors requires deep cooling.
Manufacturing processes are complex and time-consuming, increasing costs.
Pixel-to-pixel variability can cause noisy images in certain applications.
Bandpass filters may shift wavelengths depending on the angle, complicating filter use.
Lower measurement sensitivity and contrast compared to near-infrared systems.
Water absorption limits penetration depth, reducing effectiveness in some scenarios.
Medium wave quartz tube heaters excel in industrial and commercial heating. They provide significant energy savings by heating objects directly, which reduces heat loss in large spaces. These tubes support zonal heating, targeting specific areas and avoiding energy waste. Their rapid heat-up time delivers instant warmth, and their uniform, directional heating eliminates cold spots. Medium wave heaters require low maintenance and operate with high energy efficiency, making them eco-friendly and suitable for sustainable heating solutions.
Direct heating reduces utility costs.
Immediate warmth improves comfort and productivity.
Uniform heating enhances process quality.
Durable construction ensures long service life.
No combustion byproducts, supporting indoor use.
The table below outlines the primary challenges associated with medium wave IR tubes:
Disadvantage / Challenge | Explanation |
|---|---|
Difficulty curing complex part shapes | Radiation travels in straight lines; hidden surfaces may not receive enough IR exposure. |
Need for part rotation or specific oven setup | Uniform exposure often requires rotating parts or configuring emitters. |
Sensitivity to substrate emissivity | Different metals absorb IR differently; surface finish can affect absorption. |
Heat sink effects due to part mass variation | Thicker areas can draw heat away, causing uneven curing. |
Less forgiving cure window | Short cure times offer little margin for error during processing. |
Broader emission spectrum in gas IR systems | Lower purity may affect cure quality. |
Maintenance issues | Dust on reflectors can reduce system performance. |
Long wave infrared radiant tube heater, also known as far infrared heaters, operate at lower temperatures and produce comfortable, gentle heat. Their infrared waves are well absorbed by surfaces, including human skin, allowing effective heat penetration. These heaters provide uniform heating, making them ideal for saunas, incubators, and indoor comfort heating. Long wave IR tubes are energy efficient, environmentally friendly, and can heat irregular objects with high uniformity. Their non-contact heating enables quick warming of moving products, and their compact design allows easy process control.
High heating uniformity with minimal preheating time.
Environmentally friendly operation.
Suitable for irregularly shaped products.
Non-contact heating for rapid processing.
Long wave IR tubes may not deliver the intense heat required for some industrial processes. Their lower operating temperature limits their use in applications demanding rapid or deep heating. In certain scenarios, they may require additional reflectors or system adjustments to achieve optimal efficiency.
Note: Selecting the appropriate wave IR tube ensures the best balance of efficiency, comfort, and process quality for each application.
Selecting the optimal IR tube for heating requires a clear understanding of the application's demands. Each wave type—short, medium, and long—offers unique benefits. Short-wave tubes deliver rapid, high-intensity energy, making them ideal for processes that need quick temperature changes, such as powder coating or metal processing. Medium-wave tubes provide longer wavelengths and a longer lifespan, excelling in drying water- or solvent-based coatings, plastic film heating, and glass processing. Long-wave tubes suit comfort heating and gentle applications, where uniform warmth is essential.
Operators should match the wave type to the material's absorption characteristics and the desired heat penetration. For example, short-wave tubes reach higher temperatures quickly, while medium-wave tubes offer lower power density and require a larger footprint. The choice depends on the required temperature, energy efficiency, and the specific heating cycle.
Tip: Always consider the absorption properties of the target material and the process speed when selecting an IR tube.
Several critical factors influence the performance and suitability of IR tubes in various environments. The following table summarizes the main criteria to consider:
Criterion | Description |
|---|---|
Thermal Properties | Evaluate the coefficient of thermal expansion and index gradient for stability under temperature changes. |
Transmission | Select materials based on the relevant IR wave region for the application. |
Index of Refraction | Impacts optical design and system weight. |
Durability & Maintenance | Assess lifespan and maintenance needs, especially for industrial heating. |
Energy Efficiency | Short-wave tubes offer higher power density; medium-wave tubes provide longer lifespan. |
Atmospheric and operational conditions also play a significant role. Weather, fog, and dust can affect wave propagation and energy delivery. Inside industrial environments, factors such as flame radiation, burner tuning, and correct emissivity settings impact measurement accuracy and heating performance. Operators should receive training to recognize and compensate for these variables, ensuring reliable results from the infrared heating system.
Atmospheric optics phenomena can limit the effective range of wave-based heating.
Real-world conditions often degrade performance, so understanding environmental effects is essential.
Proper maintenance and installation help maintain energy efficiency and system reliability.
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology offers a comprehensive range of quartz glass IR tube heaters for diverse heating applications. Their lineup includes single and twin tube types, with cross-sections from 10mm to 18mm and twin tubes up to 15x33mm. Power ratings range from 50W to 10,000W, and lengths extend up to 4 meters for medium-wave heaters. Key products include short-wave twin tube IR emitters for rapid, high-intensity heating, medium-wave infrared heaters for lamination and drying, and carbon infrared heat lamps for uniform, gentle warmth.
Special features such as gold, white oxide, or ruby reflectors enhance energy directionality and efficiency. Accessories like stainless steel clips and clamps ensure stable installation. These products serve a wide range of applications, including printing ink curing, drying in paper mills, plastics thermoforming, and semiconductor wafer manufacturing. The company’s patented reflector coatings and strict quality control guarantee high performance and reliability in every infrared heating system.
Note: For specialized needs, Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology provides custom solutions and technical support to help operators achieve optimal heating results.
Infrared heating tubes offer efficient and reliable performance, but safe operation requires careful attention to installation and maintenance. Operators should always use high-quality quartz tubes and avoid thin-walled designs, as these reduce the risk of premature bursting. Proper sealing during production prevents air leakage, which can cause tube failure. Selecting the correct heating element model and voltage helps prevent overheating and extends the life of the equipment.
During installation, handlers must treat tubes gently to avoid breakage. They should never pull power cords forcefully or damage the quartz glass, especially at the closed end. Metal pipe clamps should allow for movement, reducing mechanical stress and preventing tube rupture. Shock-proofing and voltage stability measures help maintain safe and stable operation.
Operators should install tubes with proper spacing, orientation, and mounting clips. This setup minimizes the risk of damage and ensures effective heat dissipation. Regular cleaning prevents scale or carbon buildup, which can impede heat transfer and reduce energy efficiency. Maintaining a clean environment free from oil, water, dust, and vibration supports tube longevity.
When using gas-powered IR heaters, installers must use approved flexible gas connectors and allow for heater expansion. Venting should remain free from obstructions and flammable materials, with fire guarding in place when venting through combustible walls. Adequate fresh air intake ensures safe combustion, and exhaust systems must not recirculate gases. Operators should always follow manufacturer guidelines and safety codes, using only approved accessories.
Before installation, evaluate the site for hazards such as gas or electrical lines, combustible materials, and chemical storage. Maintain clearances from combustibles and post signage for maximum stacking heights. Protect heaters from overhead equipment and ensure accessibility for maintenance. Operators should warn occupants about high surface temperatures to prevent burns or clothing ignition.
Tip: Regular inspections and adherence to safety protocols help prevent accidents and extend the lifespan of infrared heating systems.
Infrared heating tubes provide a cleaner alternative to many traditional heating methods. These systems convert a high percentage of input energy into usable heat, reducing waste and lowering operational costs. By delivering direct radiant heat, IR tubes minimize the need for air movement, which helps maintain indoor air quality and reduces the spread of dust or pollutants.
Many IR heating solutions, such as those from Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology, operate without combustion, eliminating harmful emissions and supporting a healthier environment. When used in industrial settings, these systems can reduce overall energy consumption by up to 50% compared to conventional heaters. This efficiency not only conserves resources but also decreases the carbon footprint of manufacturing and processing facilities.
Proper installation and maintenance further enhance environmental benefits. Clean tubes and well-ventilated spaces ensure optimal energy transfer and prevent unnecessary energy loss. Operators should avoid using IR tubes in environments with hydrofluoric acid or strong alkali solutions, as these chemicals can damage the tubes and create hazardous waste.
Operators who prioritize safety and environmental stewardship help create sustainable, efficient heating systems that benefit both people and the planet.
Short, medium, and long wave IR tubes each deliver unique heat characteristics for different heating needs. Short wave tubes provide intense heat for rapid industrial processes. Medium wave tubes excel in controlled heating for plastics and glass. Long wave tubes suit comfort heating in residential or commercial applications. Material properties and environment influence tube selection. Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology offers expert guidance and reliable products. Users should evaluate their specific heating requirements to achieve optimal results.
Short wave IR tubes emit intense, high-temperature heat. Medium wave tubes provide moderate heat with balanced efficiency. Long wave IR tubes deliver gentle, uniform warmth. Each type suits different materials and applications.
Short wave and carbon infrared tubes perform best outdoors. They deliver rapid, direct heat that resists wind and cold. Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology offers IP67-rated options for patios and open spaces.
Operators should match the IR tube wavelength to the material’s absorption characteristics and the required temperature. Consulting with experts at Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology ensures optimal selection for specific needs.
Yes. IR tubes convert up to 96% of input energy into usable heat. This efficiency reduces operational costs and supports sustainable practices in both industrial and residential settings.
Medium wave IR tubes work well for plastics and glass. They provide uniform heating and precise temperature control. Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology supplies specialized quartz IR emitters for these applications.
Operators must handle tubes carefully, avoid damaging the quartz glass, and ensure proper mounting. Regular cleaning and adherence to manufacturer guidelines help maintain safe operation and extend tube lifespan.
Routine cleaning and inspection keep IR tubes operating efficiently. Operators should check for dust, scale, or carbon buildup. Using approved accessories and following maintenance schedules ensures long-term reliability.
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology provides technical support and custom solutions. Their team assists with product selection, installation, and troubleshooting for diverse heating applications.

