Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-08 Origin: Site








Halogen heat lamps deliver both safety and efficiency when users select certified products and follow proper precautions. Robust construction and recognized safety certifications such as UL, ETL, and CSA ensure that these heat lamps include essential features like thermal protectors and metal-grate guards, which help reduce fire hazards and overheating risks. Users in both residential and industrial settings benefit from the intense, direct warmth that halogen technology provides. When handled correctly, halogen heat lamp solutions offer reliable, efficient heating for a wide range of applications.

Choose certified halogen heat lamps with safety features like overheat protection and shatter-resistant tubes to reduce fire and injury risks.
Place halogen heat lamps away from flammable materials and ensure good ventilation to prevent overheating and fire hazards.
Handle bulbs carefully using gloves or cloth to avoid oils that can damage the lamp and shorten its lifespan.
Use halogen heat lamps for quick, focused heating in small areas, but consider other heaters for larger or whole-room warmth.
Clean and inspect lamps regularly to maintain efficiency, prevent dust buildup, and catch potential safety issues early.
Select the right wattage and fixture compatibility to maximize heating performance and avoid electrical problems.
Halogen heat lamps produce both light and heat instantly but use more energy than LEDs, so optimize placement and controls to save power.
A halogen heat lamp is a specialized type of incandescent lamp designed to produce both light and heat. It uses a tungsten filament enclosed in a small quartz or high-melting-point glass envelope. The envelope contains a halogen gas, such as iodine or bromine, which enables the halogen cycle. This cycle helps the filament operate at higher temperatures, resulting in brighter light and increased heat output. The compact design of these heat lamps allows for easy installation and integration into various fixtures.
Manufacturers construct halogen heat lamps from high-quality, durable materials. These lamps withstand demanding environments and offer secure lamp holding, which minimizes the risk of dislodging. The design supports compatibility with a wide range of wattages and intensities, making them suitable for many settings. Advanced products, such as those from Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology, use quartz IR emitters to deliver rapid, direct radiant heat with precise temperature control and uniform heating. These features contribute to the benefits of halogen room heaters, including reliability and efficiency.
The operating principle of a halogen heat lamp centers on the heating of a tungsten filament by an electric current. The filament emits both light and heat. The presence of halogen gas inside the bulb enables the halogen cycle, which redeposits evaporated tungsten back onto the filament. This process allows the filament to reach higher temperatures, producing more intense heat and extending the lamp’s lifespan. Unlike other lighting technologies, such as LEDs or CFLs, halogen heater models generate significant heat as a primary function, making them effective for focused heating tasks.
Infrared heat lamp technology, as seen in advanced quartz IR emitters, further enhances efficiency by delivering heat directly to objects and surfaces. This direct radiant heating reduces heat loss and operational costs. The use of UV-absorbing glass filters or coatings also improves safety by reducing ultraviolet exposure. Protective housings and grids help prevent fire hazards, supporting the safe use of halogen room heaters in both residential and industrial environments.
Halogen heat lamps demonstrate versatility in applications across residential and industrial settings. Their robust construction and efficient heat delivery make them ideal for a variety of uses. The table below highlights some common applications and their benefits:
Application Setting | Common Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Residential | Halogen room heaters, accent lighting, table lamps, food heat lamps | Enhanced brightness, improved color rendering, instant heat, energy efficiency |
Industrial | Halogen heater units for outdoor areas, construction sites, stage lighting, drying | Durability, weather resistance, wide coverage, rapid heating, consistent performance |
Halogen heater products, including heat lamp types like quartz IR emitters, support processes such as paint drying, plastic molding, and even agricultural heating. In homes, halogen room heaters provide quick, focused warmth and improved lighting for detailed tasks. The benefits of halogen room heaters include longer lifespan, reduced replacement frequency, and better energy efficiency compared to traditional incandescent lamps. Their versatility in applications ensures that users can rely on these heat lamps for both comfort and productivity.
Tip: When selecting halogen heater solutions, consider certified products with advanced safety features for optimal performance and peace of mind.
Safety Features
Halogen heat lamps incorporate a range of safety features to protect users and property. Manufacturers design these lamps with robust materials and advanced engineering to minimize risks. The following safety measures are commonly found in modern halogen heat lamps:
Use of halogen-approved fixtures that fully contain the lamp in case of breakage.
Shatter-resistant tubes to prevent glass fragments from causing injury.
Automatic shut-off mechanisms that activate if the lamp overheats.
Secure lamp holding to prevent dislodging and electrical arcing.
UV-absorbing glass filters or coatings to reduce ultraviolet exposure.
External fuses for added electrical safety.
Clear labeling for wattage, voltage, and burn position to prevent misuse.
These safety features help reduce the risk of burns, electrical accidents, and fire. They also support compliance with industry standards and certifications.
Overheat protection stands as a critical component in halogen heat lamp design. This feature automatically shuts off the lamp if it reaches unsafe temperatures. By interrupting the power supply, overheat protection prevents damage to the lamp and surrounding materials. It also reduces the likelihood of fire, especially in environments where lamps operate for extended periods. Many certified products include thermal sensors or built-in thermostats to monitor temperature and activate this safety measure when necessary.
Shatter resistance enhances user safety by minimizing the risk of injury from broken glass. Manufacturers use reinforced quartz or special coatings to strengthen the lamp envelope. If the lamp experiences impact or sudden temperature changes, the shatter-resistant design helps contain fragments. This feature is especially important in industrial settings, where accidental contact or vibration may occur. Shatter resistance also supports safe handling during installation and maintenance.
Many users ask, "are halogen heaters safe?" Modern halogen heaters offer a high level of safety when users follow recommended safety precautions. Recent studies and safety reports indicate that halogen heaters do not pose direct toxicological or carcinogenic risks during normal operation. The main health concerns relate to burn risks from exposed hot surfaces and the fragility of quartz tubes. Manufacturers have addressed these issues by introducing shatter-resistant tubes and automatic shut-off mechanisms since 2022.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Safety Concerns | Burn risks from exposed hot surfaces; fragility of quartz tubes affecting durability. |
Safety Improvements | Introduction of shatter-resistant tubes and automatic shut-off mechanisms since 2022. |
Market Trends | Growing demand driven by energy efficiency, compact design, and versatility in residential and industrial use. |
Risk Level Indication | No recent studies highlight elevated risk levels beyond burn hazards; no toxicological risks directly linked to halogen heaters themselves. |
User Recommendations | Use models with modern safety features and be aware of burn hazards. |
Note: Halogen heaters remain safe for both residential and industrial use when users select certified models and follow all safety measures. Always keep the lamp away from children and pets, and avoid touching the lamp surface during operation.
Halogen heat lamps generate intense heat, which can create fire risks if not managed properly. The most common causes of fire hazards include improper installation, insufficient ventilation, and placing lamps too close to flammable materials. High heat output can ignite nearby objects such as paper, cloth, or plastic. Recessed halogen lights require special attention, as poor ventilation can trap heat and increase the risk of fire.
To mitigate these risks, users should:
Ensure installation by qualified electricians, especially for recessed lamps.
Maintain at least 50 cm distance from combustible items.
Use heat-resistant materials and ensure adequate ventilation around the lamp.
Follow all manufacturer safety instructions carefully.
Avoid self-installation of recessed spotlights.
Perform regular maintenance to keep fixtures clean and free from obstructions.
Never leave halogen lamps unattended, particularly near children, pets, or paper shades.
Proper ventilation plays a crucial role in preventing overheating and reducing fire hazards. Users should always check that air can circulate freely around the lamp and that no objects block heat dissipation. Regular inspection and cleaning further support safe operation.
Certification Body | Role / Scope |
|---|---|
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) | Certifies electrical products for safe use, including hazardous locations under IECEx and OSHA NRTL programs |
TUV Rheinland | Recognized certifier for electrical product safety, including halogen heat lamps |
OSHA NRTL Program | Qualifies laboratories to certify products for workplace safety |
IECEx Scheme | Certifies products for use in hazardous locations with explosive gas or dust environments |
Intertek | Accepted Certification Body under IECEx and recognized by OSHA NRTL |
FM Approvals | Accepted Certification Body under IECEx and recognized by OSHA NRTL |
These certifications confirm that halogen heat lamps meet strict safety requirements for electrical safety and hazardous environment use. Selecting certified products and following all safety precautions ensures reliable performance and minimizes fire risk.
Correct placement of halogen heat lamps plays a vital role in ensuring safety and maximizing efficiency. Users should position lamps away from flammable materials such as curtains, bedding, clothing, and paper. Placing the lamp on a stable, level surface prevents tipping and accidental contact. Maintaining proper ventilation around the lamp reduces the risk of overheating and rapid lamp failure. Users must avoid placing items on or around the lamp to allow heat to dissipate freely.
Safety tips: Always supervise children and pets near halogen heat lamps to prevent accidents or injuries.
Manufacturers recommend using halogen lamps only in approved fixtures that fully contain lamp parts in case of breakage. Users should never allow one lamp to directly expose another, as this can lead to overheating and shortened lamp life. Operating the lamp only in the indicated burn position helps prevent stress and damage to the filament. Proper placement supports both safety precautions and optimal heat distribution.
Electrical safety remains a top priority during installation and setup. Users must turn off electrical power before inserting, removing, or cleaning the lamp. Wearing clean gloves or using a lint-free cloth prevents oil contamination, which can cause breakage or shorten lamp life. Securely affixing the lamp in the socket prevents electrical arcing, overheating, and premature failure.
The following ordered list outlines recommended installation and setup procedures:
Unplug the fixture and allow the bulb to cool for at least 10 minutes before handling.
Remove heat guards or protective covers carefully, noting their placement for reassembly.
Use a firm but gentle grip to unscrew the bulb; wear gloves or use a cloth to avoid direct contact.
For bayonet fittings, push in and turn to remove; seek professional help if stuck.
Use appropriate safety equipment for hard-to-reach bulbs or consult professionals.
Wrap old bulbs in paper before disposal to prevent injury and check local regulations.
Users should use lamps only at specified wattage and voltage in appropriately rated fixtures. Avoid exceeding rated voltage or using dimmers that may increase voltage. Always use an external fuse when required. Verifying correct wiring and ensuring secure connections help prevent voltage irregularities and damage. Switch breaks must occur on the hot wire, not the neutral, to maintain electrical safety.
Proper ventilation during installation and setup prevents overheating and supports long-term reliability. Users should check that air can circulate freely around the lamp and that no objects block heat dissipation.
Regular cleaning of halogen heat lamps ensures ongoing safety and efficient operation. Dust buildup on the bulb or lampshade can cause overheating and reduce lamp life. Users should clean any dirt, oil, or lint from the bulb surface with alcohol and a lint-free cloth or tissue. Never touch the bulb surface or inside reflectors with bare hands, as fingerprints can create hot spots and lead to lamp failure.
The following maintenance practices support safety precautions:
Clean the bulb and lampshade regularly to avoid dust accumulation.
Use only recommended cleaning materials to prevent damage.
Turn off and unplug the lamp before cleaning to avoid electrical hazards.
Maintaining a clean lamp surface helps prevent uneven heating and deposits inside the quartz envelope. This practice reduces the risk of rapid lamp failure and supports proper ventilation.
Routine inspection helps identify potential issues before they become hazards. Users should monitor the lamp's operating temperature and turn it off immediately if it becomes excessively hot or emits unusual smells. Checking for loose electrical connections or wiring issues ensures safe operation. Replace lamp holders and sockets if needed to prevent electrical arcing and overheating.
The table below summarizes common user-reported issues and prevention methods:
Common Issue | Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
Rapid lamp failure due to overheating | Poor ventilation or focused heat | Ensure proper ventilation; avoid enclosed fixtures |
Voltage spikes causing failure | Voltage surges or unstable supply | Use surge suppression devices; check wiring |
Dirty or contaminated lamp surfaces | Fingerprints or dust | Clean lamps carefully; avoid contamination |
Loose electrical connections | Improper wiring or connections | Verify wiring; ensure secure connections |
Incorrect lamp orientation | Mounting not as specified | Mount lamps as directed by manufacturer |
Users should always use quality, authentic lamps from reputable manufacturers to avoid premature failure. Operating the lamp only in the indicated burn position and maintaining temperature limits further support safety precautions.
Note: Turn off and unplug the lamp when not in use to ensure safety and extend lamp life.
Halogen heat light technology delivers intense radiant heat by operating at elevated halogen bulb temperature levels. The tungsten filament inside the bulb reaches high temperatures, emitting both visible light and infrared radiation. This process allows heat lamps to provide rapid spot heating, making them suitable for applications that require immediate warmth. Halogen heat lamps excel in environments where direct, focused heat is necessary, such as workspaces, food warming stations, and industrial drying processes. The high halogen bulb temperature ensures consistent heat output, supporting optimal performance in demanding settings.
Halogen heat light systems consume electrical energy at rates similar to other electric resistance heaters. However, halogen heat lamps emit a portion of their energy as light, which reduces their overall heating efficiency for space heating. While a watt of electricity produces the same amount of heat in any resistance heater, halogen lamps direct some energy toward illumination. This characteristic makes halogen heat lamps less efficient than dedicated electric heaters or heat pumps, which convert nearly all input energy into heat. Halogen heat lamps primarily warm surfaces through radiant energy, requiring line-of-sight for effective heating. As a result, their energy efficiency depends on placement and application. For spot heating or tasks that benefit from both light and heat, halogen heat light solutions offer practical advantages.
Proper sizing and strategic placement play a crucial role in optimizing halogen bulb performance and achieving optimal performance. Users should select heat lamps with wattages that match the size and requirements of the space. Placing halogen heat light fixtures to target specific areas ensures that radiant energy reaches intended surfaces, minimizing wasted energy. Conducting load calculations and designing circuits to handle higher power consumption supports safety and efficiency. In industrial settings, thermal mapping helps identify heat hotspots and guides fixture placement for even coverage. Adequate ventilation and heat management techniques, such as using heat sinks and ensuring airflow, prevent excessive halogen bulb temperature and protect surrounding materials.
Users can enhance the efficiency of halogen heat light systems by following several practical strategies:
Use smart lighting controls, including timers, occupancy sensors, and dimmers, to reduce unnecessary operation and energy consumption.
Prefer task lighting over ambient lighting to focus heat and light where needed, lowering the number of active heat lamps.
Maintain fixtures by cleaning dust and debris regularly, which supports consistent halogen bulb temperature and optimal performance.
Integrate reflective surfaces and lighter finishes in the environment to improve light distribution, allowing for fewer or dimmer heat lamps.
Follow manufacturer installation guidelines and local codes to ensure secure mounting and compatibility with controls.
Replace bulbs promptly to maintain efficiency and lighting quality.
Leverage the rapid warm-up and high color rendering of halogen heat light for applications that demand quick illumination and precise color fidelity.
Tip: Conduct lighting audits and thermal mapping to optimize fixture placement and usage, ensuring maximum energy efficiency and safety.
Halogen heat light technology offers reliable heat output and flexibility when users apply best practices for sizing, placement, and operation. By managing halogen bulb temperature and integrating smart controls, users can achieve optimal performance and energy efficiency in both residential and industrial environments.
Halogen heat light technology impacts the environment in several important ways. The most significant factor involves energy consumption. Halogen heat light systems convert a large portion of electricity into heat rather than light. This process leads to lower energy efficiency compared to modern alternatives such as LEDs. As a result, halogen heat light products require more power to achieve the same brightness or heating effect.
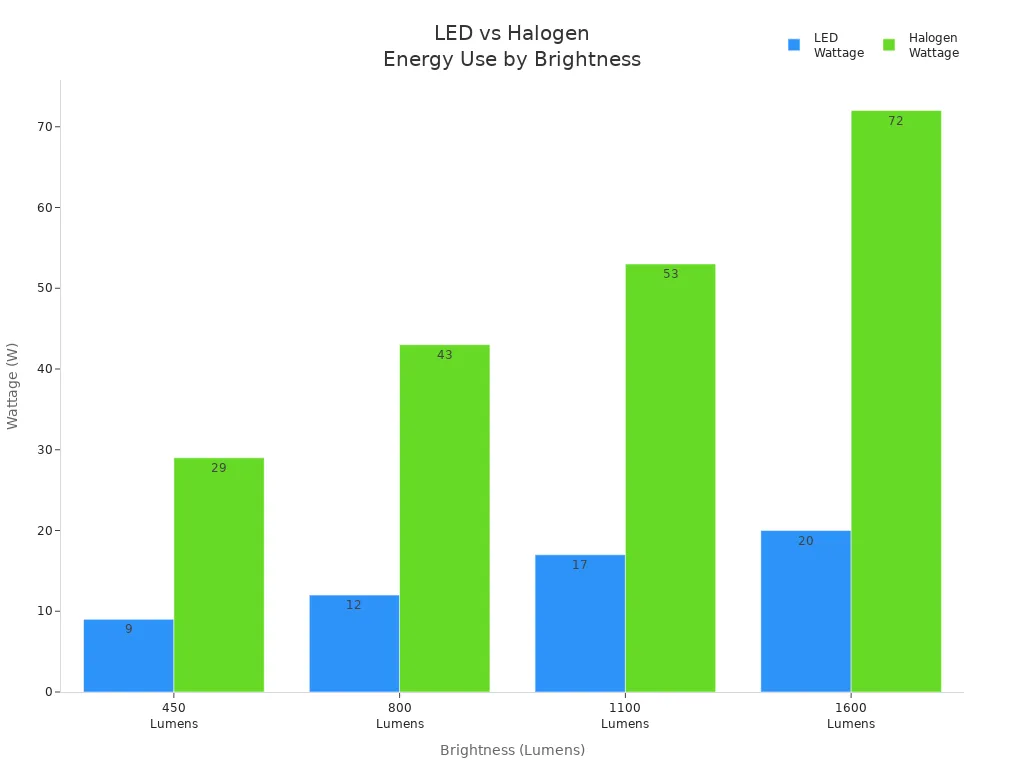
The following table compares the wattage required by halogen and LED lamps to produce similar brightness levels:
Brightness (Lumens) | Approximate LED Wattage | Approximate Halogen Wattage |
|---|---|---|
450 | 9 W | 29 W |
800 | 12 W | 43 W |
1100 | 17 W | 53 W |
1600 | 20 W | 72 W |
This data shows that halogen heat light systems consume much more energy than LEDs for the same output. The higher energy use translates directly into increased greenhouse gas emissions, especially in regions where electricity comes from fossil fuels. The environmental impact grows as more halogen heat light units operate over time.
Halogen heat light products also present challenges at the end of their life cycle. The presence of halogen gas and other hazardous materials requires careful disposal. Improper handling can lead to environmental contamination. In contrast, LEDs last longer and reduce waste, further improving overall energy efficiency and reducing the frequency of replacements.
Switching from halogen heat light to more efficient technologies can significantly lower carbon emissions. Studies show that widespread adoption of LEDs could reduce global greenhouse gas emissions by gigatons of CO2 equivalent by 2050. The higher efficiency and longer lifespan of LEDs make them a more sustainable choice for both lighting and heating applications.
Note: Users who prioritize energy efficiency and environmental responsibility should consider the full life cycle of their heating and lighting solutions. Proper disposal and recycling of halogen heat light products help minimize their environmental footprint.
Selecting the right heat lamps for a specific environment requires careful consideration of several factors. Users should evaluate the size of the bulb, as the diameter directly affects fit and application. The place of installation plays a significant role. For example, outdoor floodlights and recessed lighting demand different lamp types and sizes. Cost remains an important factor, with halogen room heaters offering a lower upfront price compared to other technologies.
Brightness and color temperature also influence the choice. Users can select from warm white, soft white, or bright white to match the ambiance of the space. Wattage determines the brightness, so it is important to choose a level that fits the room’s needs. Fixture compatibility ensures the halogen room heater fits securely and operates safely. Heat generation should not be overlooked, as halogen room heaters emit significant warmth, which can benefit or challenge certain environments.
Other considerations include:
Affordability and long-term costs, as halogen room heaters may consume more energy over time.
Application environment, such as indoor or outdoor use, task type, and portability.
Safety features, including shatter resistance and overheat protection, which are essential for both residential and industrial settings.
Tip: Always match the halogen room heater to the fixture and application for optimal performance and safety.
Proper installation of halogen room heaters ensures both safety and efficiency. Users should verify that the lamp fixture is compatible with halogen bulbs, as high heat output can cause overheating if the fixture is not suitable. The bulb base and socket type must match to prevent electrical hazards. Wattage should never exceed the fixture’s maximum rating, as this can lead to excessive heat buildup.
Adequate ventilation around the fixture is crucial. Halogen room heaters can reach temperatures up to 1300℉ (700℃), so avoid enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces. Fixtures made from heat-resistant materials, such as metal or glass, provide better durability and safety. Voltage compatibility also matters; users should check if the system requires 12V or 230V and use the correct transformer if needed.
Best practices include:
Adhering to local electrical codes and safety standards.
Selecting lamp holders designed for halogen room heaters, considering both type and material.
Using proper wiring techniques and secure connections.
Inspecting all components for damage before installation.
Labeling circuits for easy maintenance.
Documenting the installation process for future reference.
Note: Regular maintenance checks after installation help ensure the continued safe operation of halogen room heaters.
Routine maintenance extends the lifespan and maintains the efficiency of halogen room heaters. The typical halogen bulb lasts between 450 and 1,000 hours, but factors such as heat output, vibration, and voltage fluctuations can affect longevity. Users should clean the lamp surface regularly to prevent dust buildup, which can reduce light intensity and cause thermal stress.
Key maintenance practices include:
Use professional installation services to ensure proper fitting.
Always wear gloves when handling bulbs to avoid transferring oils that can cause hot spots.
Disconnect power before performing any maintenance.
Clean lamp surfaces and fixtures to maintain heat dissipation.
Monitor for signs of dimming or degradation and replace bulbs promptly.
Ensure stable voltage supply to protect the filament.
Check for moisture in fixtures to prevent electrical damage.
Handle bulbs carefully to avoid physical damage.
Manufacturers recommend using high-quality bulbs and maintaining a stable electrical system. Proper sealing of fixtures protects against moisture and environmental factors. Regular replacement before complete failure ensures safety and consistent performance.
Regular inspection and cleaning of halogen room heaters help maintain their efficiency and extend their service life.
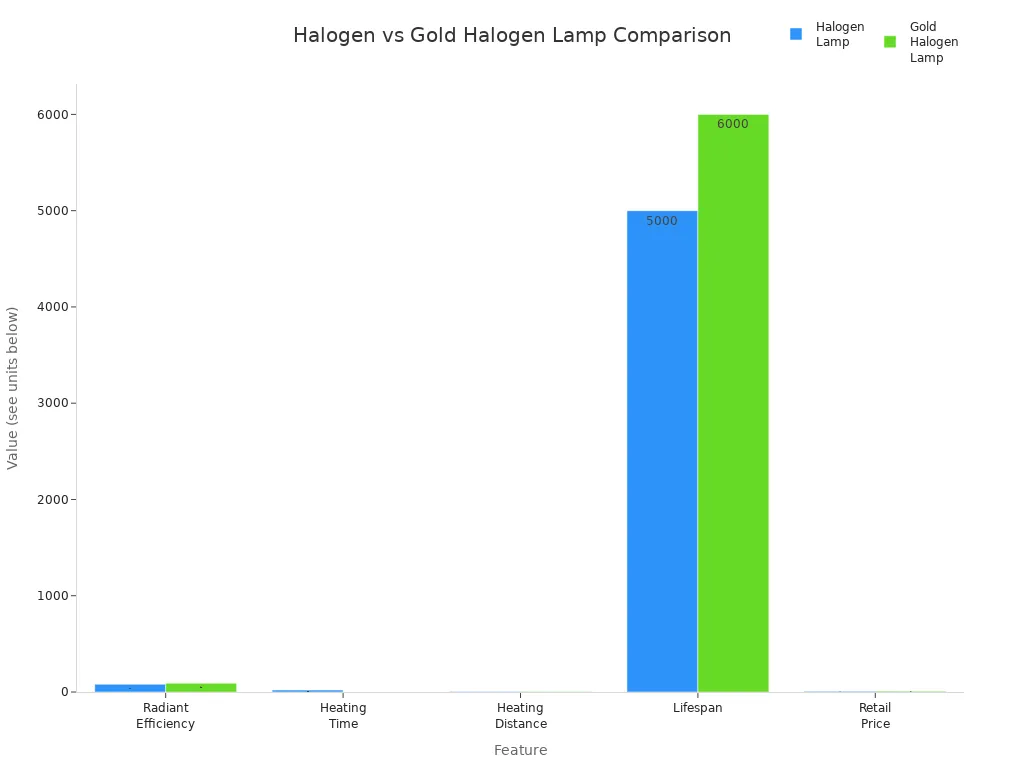
Halogen heater technology belongs to the broader category of infrared heaters. Both types use radiant energy to warm objects and people directly, rather than heating the air. This approach increases energy efficiency, especially in spaces where quick, targeted warmth is needed. Halogen heat lamps typically reach about 80% radiant efficiency, while advanced gold halogen lamps can achieve up to 92%. Gold halogen lamps also provide instant heat within one second and cover greater distances, making them suitable for larger or outdoor areas.
Feature | Halogen Lamp | Gold Halogen Lamp |
|---|---|---|
Radiant Efficiency | 80% | 92% |
Heating Time | ~20 seconds | Instant (1 second) |
Heating Distance | 4-5 meters | 5-6 meters |
Lifespan | ~5000 hours | ~6000 hours |
Retail Price | 5-8 USD | 8-10 USD |
Infrared heaters, including halogen heat lamps, offer safety advantages. They emit no harmful gases or UV radiation. Many models include features like automatic shut-off and weatherproof designs. The Heliosa 66 infrared halogen heater, for example, demonstrates high efficiency and low operational costs, making it a reliable choice for both indoor and outdoor use.
Incandescent lamps and halogen heat lamps share similar operating principles. Both generate heat and light by passing electricity through a tungsten filament. However, halogen heater models operate at higher temperatures, producing a whiter and brighter light. This higher temperature also means that halogen heat lamps emit more concentrated heat from a smaller glass envelope.
Both lamp types consume similar energy at the same wattage.
About 90% of their input power becomes heat.
Halogen heat lamps offer better color rendering and longer lifespan.
Incandescent lamps have a lower upfront cost but higher long-term energy use.
Halogen heater products provide more intense, focused heat, making them preferable for spot heating.
Halogen heat lamps also convert a slightly higher percentage of energy into visible light, improving overall efficiency compared to standard incandescent bulbs.
Electric heaters come in several forms, such as convector heaters, oil-filled radiators, and fan heaters. Halogen heater units differ by providing instant, direct infrared heat, which targets objects and people rather than warming the entire room. This method reduces operational costs, with halogen heat lamps averaging about £0.33 per hour, while fan heaters can cost up to £0.55 per hour.
Aspect | Halogen Heaters | Other Electric Heaters (e.g., Convector, Oil-filled Radiators) |
|---|---|---|
Heating Method | Instant, direct infrared heat targeting objects | Warm air convection or retained heat via oil-filled elements |
Operational Cost | Approximately £0.33 per hour (low cost) | Generally higher; e.g., fan heaters ~£0.55 per hour |
Heating Coverage | Limited to small areas or direct line of sight | Better for whole-room heating |
Safety Features | General electric heater safety applies | Thermostats, automatic shut-off, tip-over switches, cool-touch exteriors |
Suitability | Best for short-term, small space use | Suitable for continuous, whole-room heating |
Additional Features | Adjustable wattage, reflective elements | Thermostats and timers for energy savings and safety |
Halogen heat lamps excel in providing quick warmth for small spaces or intermittent use. Other electric heaters often include advanced safety features such as thermostats, tip-over switches, and cool-touch exteriors, making them suitable for continuous, whole-room heating.
Tip: Choose halogen heater solutions for rapid, focused heating in small areas, and consider other electric heaters for larger, continuous heating needs.
Halogen heat lamps offer a unique set of advantages and disadvantages when compared to other common heating technologies. Understanding these factors helps users make informed decisions for both residential and industrial applications.

Instantaneous Heat Output: Halogen heat lamps deliver radiant warmth almost immediately after activation. This feature makes them ideal for spot heating and environments where quick temperature changes are necessary.
Compact and Versatile Design: The small size of halogen bulbs allows installation in tight or specialized spaces. Users can employ these lamps in unique applications where larger heaters may not fit.
Dimmable Functionality: Many halogen heat lamps support dimming. This capability enables users to adjust both light and heat output to match specific needs.
Low Initial Cost: Halogen heat lamps generally cost less upfront than many alternative heating solutions. This affordability appeals to budget-conscious buyers.
No Harmful Emissions: These lamps do not produce smoke or carbon monoxide, supporting a safer indoor environment.
Lower Energy Efficiency: Halogen heat lamps consume more electricity than modern alternatives such as advanced infrared heaters or LEDs. Extended use can lead to higher operational costs.
Limited Heating Range: These lamps excel at targeted heating but struggle to warm large spaces effectively. Users may need multiple units for broader coverage.
Sensitivity to Handling: Oils from skin contact can damage the quartz envelope, reducing lamp lifespan. Proper handling with gloves or a cloth is essential.
Aesthetic Limitations: The enclosed quartz design lacks the traditional look of classic incandescent bulbs. Some users may prefer the appearance of other lighting technologies.
Heat Management Required: Halogen heat lamps generate significant surface heat. Users must ensure proper placement and ventilation to avoid safety hazards.
The table below summarizes the main pros and cons of halogen heat lamps and compares them with other heating technologies:
Aspect | Halogen Heaters – Pros | Halogen Heaters – Cons | Comparison with Other Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
Energy Efficiency | Instant heat; effective for small areas | Costly for long-term use; less efficient for large spaces | Advanced infrared heaters offer higher efficiency |
Heating Characteristics | Quick, targeted warmth; portable | Limited to spot heating; not suitable for whole-room heating | Short wave IR heaters excel at space heating |
Safety | Do not emit harmful gases | Surface can become very hot; careful handling required | Many alternatives include cool-touch exteriors |
Environmental Impact | No smoke or carbon monoxide emissions | Higher energy consumption increases carbon footprint | LEDs and modern IR heaters are more eco-friendly |
Installation | Simple and flexible installation | Sensitive to oils; requires careful handling | Some alternatives require professional setup |
Tip: Users seeking rapid, focused heating in small spaces benefit most from halogen heat lamps. For larger areas or continuous use, consider more energy-efficient options such as advanced infrared heaters.
Halogen heat lamps deliver reliable warmth when users follow essential safety steps. Key precautions include keeping lamps away from flammable materials, choosing models with automatic shut-off, and cleaning units regularly. Robust construction and safety certifications from recognized laboratories ensure dependable operation and reduce fire risks. For greater efficiency, users can install dimmers or timers and consider upgrading to ENERGY STAR-certified lighting. Regular inspection and responsible use help extend lamp life and maintain safety.
Select certified, high-quality halogen heat lamps for safe, efficient heating in any environment.
Users should check for certifications like UL, TUV, CSA, or ETL. These marks indicate that the lamp meets strict safety standards. Certified products offer better protection against electrical hazards and fire risks.
Manufacturers recommend inspecting halogen heat lamps every three months. Users should clean the lamp and check for signs of damage or loose connections. Regular maintenance helps ensure safe and efficient operation.
Yes, many halogen heat lamps suit outdoor use. Users should select models with weatherproof ratings, such as IP65 or IP67. Outdoor-rated lamps resist moisture and dust, making them ideal for patios, construction sites, and gardens.
Halogen heat lamps provide rapid, direct heating. They support processes like paint drying, plastic molding, and glass manufacturing. Their robust construction and high efficiency make them reliable for demanding industrial environments.
Halogen heat lamps offer instant, focused heat. They use more energy than LEDs but outperform traditional incandescent bulbs. For spot heating, halogen lamps deliver efficient results, especially when users optimize placement and usage.
Users should turn off power before installation. They must use compatible fixtures and avoid touching the bulb with bare hands. Proper placement away from flammable materials reduces fire risk. Always follow manufacturer instructions for safe setup.
Users should avoid frequent switching on and off. They must keep the lamp clean and handle it with gloves. Stable voltage supply and proper ventilation also extend lamp life.
Tip: Always choose certified, high-quality halogen heat lamps for the best safety and performance.

