Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-08 Origin: Site








Consumers and industries seek the most energy-efficient option for heating, including ceramic heaters, oil-filled radiators, panel heaters, heat pumps, far infrared heaters, quartz IR emitters, and led solutions. Halogen infrared lamp alternatives deliver efficient heat, improved safety, and cleaner warmth. Studies from Japanese smart communities show that modifying heat use patterns and adopting energy-efficient lighting and energy-efficient light bulb choices can achieve significant energy savings and reduce emissions. Selecting energy-efficient options and energy-saving light bulbs maximizes savings, efficiency, and environmental benefits. Energy-efficient bulbs and led technologies represent the most energy-efficient option for both lighting and heat.
Halogen infrared lamps use a lot of energy, have short lifespans, and pose safety risks like burns and fire hazards.
Energy-efficient alternatives like ceramic heaters, oil-filled radiators, panel heaters, heat pumps, far infrared heaters, and quartz IR emitters offer safer and cleaner warmth.
Ceramic heaters provide fast heat with built-in safety features, ideal for small to medium rooms.
Oil-filled radiators deliver silent, steady heat and remain safe with enclosed heating elements.
Heat pumps are highly efficient, safe, and reduce heating costs, but need professional installation.
LED and CFL bulbs save energy and last longer than halogen lamps, with LEDs being the most efficient and eco-friendly.
Choosing the right heater depends on room size, usage patterns, budget, and safety needs to maximize comfort and savings.
Using energy-efficient heating and lighting reduces carbon emissions, lowers bills, and protects the environment.
Consumers and industries increasingly seek alternatives to halogen infrared lamp technology due to several significant drawbacks. Regulatory frameworks and government standards now target energy efficiency and environmental safety, pushing manufacturers to innovate and improve heating solutions. Fluctuating prices of raw materials such as tungsten and quartz also affect production costs, making halogen infrared lamp products less attractive. The availability of substitutes like LED and CFL lighting increases competition and encourages the development of more efficient and eco-friendly options.
Halogen infrared lamp products often have a high initial cost compared to other heating technologies.
Their energy consumption is much higher than that of LED alternatives, sometimes requiring up to ten times more power for the same brightness.
Frequent replacements are necessary due to shorter lifespans, typically between 2,000 and 4,000 hours, which leads to increased waste.
The substantial heat output can raise ambient temperatures, making them less suitable for prolonged use in many environments.
Market research shows that the demand for energy-efficient and sustainable heating solutions continues to rise. Manufacturers respond by offering products that deliver efficient warmth, lower energy consumption, and improved safety.
Halogen infrared lamp usage presents notable safety risks. These lamps operate at extremely high temperatures, often between 900°F and 1,200°F, which can ignite nearby combustible materials such as curtains, towels, or clothing. Documented incidents include house fires, property damage, and even fatalities. Experts recommend keeping lamps away from flammable materials and using wire grills or newer, cooler models to reduce risk.
Halogen infrared lamp products can cause serious burns and fire hazards if not handled properly.
Electrical shock hazards exist due to high ignition voltage, requiring careful installation and operation.
Emission of UV and IR radiation may result in severe skin burns or permanent eye damage.
Fragile bulbs can explode or shatter, scattering hot glass fragments and igniting fires.
Some universities have banned certain halogen lamp styles in dormitories due to these safety concerns. Users often underestimate the heat generated, increasing the risk of accidents.
The environmental footprint of halogen infrared lamp technology is another major concern. Their high energy consumption leads to increased carbon emissions, especially when powered by fossil fuels. The shorter lifespan of halogen bulbs results in more frequent replacements, contributing to landfill waste. In contrast, LED alternatives offer longer life, lower energy consumption, and contain no hazardous materials, making them a more eco-friendly choice.
Halogen infrared lamp products are less sustainable due to higher energy use and heat generation.
Increased waste from frequent bulb replacements negatively affects the environment.
Efficient alternatives like LEDs and advanced infrared heaters help reduce energy consumption and support a cleaner environment.
Choosing efficient and eco-friendly heating solutions benefits both the user and the environment, reducing costs and minimizing negative impacts.
Ceramic heaters use a ceramic element that heats up when electricity passes through it. A fan often blows air over the hot ceramic plates, distributing warmth quickly throughout the room. This technology allows for rapid heat output and precise temperature control, making it suitable for heating spaces of various sizes.
Ceramic heaters offer several safety features. The ceramic element does not get as hot as exposed metal coils, reducing the risk of burns. Many models include tip-over protection and overheat shut-off, which further enhance safety in homes with children or pets. The outer casing remains cool to the touch, minimizing accidental contact injuries.
Ceramic heaters stand out as efficient options for supplemental heating. They convert nearly all the electrical energy into heat, ensuring minimal waste. Many units carry energy star certification, which guarantees high efficiency and lower energy consumption. Users can adjust settings to match their comfort needs, optimizing energy use and reducing costs.
Pros:
Fast and direct heat output
Lightweight and portable
Built-in safety features
Energy-efficient alternatives for small to medium rooms
Cons:
Less effective for large areas
Fan noise may be noticeable in quiet environments
Oil-filled radiators use electricity to heat oil sealed inside the unit. The heated oil circulates through columns, radiating warmth into the room. These heaters do not use fans, so they operate silently and provide a steady, gentle heat.
Oil-filled radiators excel in safety. The heating element is fully enclosed, so there are no exposed high-temperature parts. This design makes them safer around children and pets. While the surface can become warm, it rarely reaches temperatures that cause burns. Many models include tip-over and overheat protection for added peace of mind.
Oil-filled radiators convert electrical energy into heat with nearly 100% efficiency. The oil retains heat for a long time, allowing the unit to continue warming the room even after it switches off. This sustained heat output can help maintain comfort with lower thermostat settings, reducing overall energy use. Many models meet energy star certification standards, ensuring efficient operation.
Pros:
Silent operation
Long-lasting, even heat
No exposed heating elements
Efficient for continuous heating
Cons:
Slower to reach desired temperature
Heavier and less portable than other heaters
Panel heaters use electric elements embedded in a flat panel to emit infrared heat. These panels can be mounted on walls or placed on stands. They warm objects and people directly, rather than heating the air, which results in instant comfort.
Panel heaters provide a safe heating solution. The surface temperature remains moderate, reducing the risk of burns. There are no moving parts or exposed elements, making them suitable for homes with children or pets. Many models include overheat protection and energy star certification for added safety and efficiency.
Panel heaters deliver efficient warmth by directly transferring energy to surfaces and occupants. This method reduces energy loss and ensures quick comfort. Users benefit from lower energy bills and consistent heat output. The technology supports energy-efficient alternatives for both residential and commercial spaces.
Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages / Limitations |
|---|---|---|
Heating Speed | Instant heat output to people and objects | Higher upfront cost than convection heaters |
Heating Distribution | Even heating via infrared rays | Limited range in large or complex rooms |
Noise Level | Silent operation | N/A |
Eco-friendliness | No fuel burning, no fumes, no allergens | N/A |
Room Suitability | Ideal for small to medium rooms | Less effective in large or irregular spaces |
Safety | Moderate surface temperature, no exposed elements | N/A |
Cost | Potential long-term savings due to efficiency | Higher initial investment |
Panel heaters offer a blend of safety, efficiency, and comfort, making them a popular choice for modern homes and offices.
Heat pumps transfer heat from one place to another using a refrigeration cycle. In heating mode, they extract heat from the outside air, ground, or water and move it indoors. This process works even in cold weather, making heat pumps a versatile solution for both residential and industrial spaces. Unlike traditional heaters that generate heat by burning fuel or using electric resistance, heat pumps use electricity to move existing heat, which makes them highly efficient.
Heat pumps offer a strong safety profile. They do not use open flames or reach high surface temperatures, which reduces the risk of burns or fire. Most modern units include automatic shut-off features and temperature sensors to prevent overheating. While specific safety records for heat pumps as alternatives to halogen infrared lamps are limited, industry reports recognize heat pumps as a competitive and safe option in the heating market.
Heat pumps stand out for their energy efficiency. They deliver more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume. The following table shows efficiency metrics for different types and sizes of heat pumps:
Equipment Type | Size Category (Btu/h) | Test Condition | Efficiency Metric | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Air Cooled (Cooling Mode) | 65,000 - <135,000 | - | EER | 11.0 |
Air Cooled (Cooling Mode) | 65,000 - <135,000 | - | IEER | 14.1 |
Air Cooled (Cooling Mode) | 135,000 - <240,000 | - | EER | 10.6 |
Air Cooled (Cooling Mode) | 135,000 - <240,000 | - | IEER | 13.5 |
Water Source (Cooling Mode) | 65,000 - <135,000 | 86ºF entering water | EER | 13.0 |
Groundwater Source (Cooling Mode) | <135,000 | 59ºF entering water | EER | 18.0 |
Air Cooled (Heating Mode) | 65,000 - <135,000 | 47ºF db/43ºF wb outdoor air | COP | 3.4 |
Air Cooled (Heating Mode) | 65,000 - <135,000 | 17ºF db/15ºF wb outdoor air | COP | 2.25 |
Water Source (Heating Mode) | <135,000 | 68ºF entering water | COP | 4.3 |
Groundwater Source (Heating Mode) | <135,000 | 50ºF entering water | COP | 3.7 |
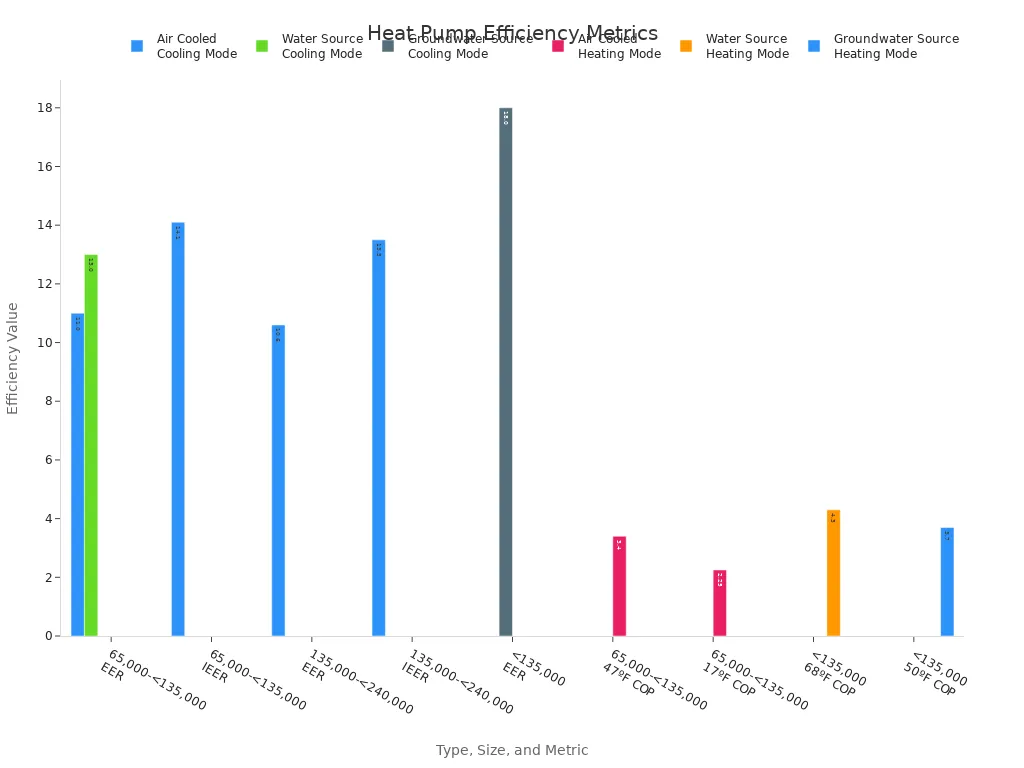
Heat pumps often achieve energy star certification, which confirms their efficient operation and lower energy consumption. Many users experience significant reductions in heating costs and carbon emissions.
Pros:
Highly efficient for both heating and cooling
Lower operating costs due to reduced energy use
Safe operation with no combustion or exposed heating elements
Suitable for a wide range of climates and building types
Cons:
Higher upfront installation cost
Efficiency can decrease in extremely cold climates
Requires professional installation and maintenance
Heat pumps provide a reliable, efficient, and safe alternative to halogen infrared lamps, especially for those seeking long-term energy savings.
Far infrared heaters use advanced technology to emit infrared radiation in the far end of the spectrum. This type of heat penetrates deeper into objects and people, providing a gentle and even warmth. Unlike traditional heaters that warm the air, far infrared heaters deliver direct heat to surfaces, which improves comfort and reduces energy loss.
Manufacturers design far infrared heaters with safety in mind. The surface temperature remains moderate, which lowers the risk of burns. Many models include overheat protection, tip-over switches, and child-safe features. These heaters do not produce open flames or hot coils, making them suitable for homes, offices, and healthcare settings.
Far infrared heaters excel in energy efficiency. They convert nearly all the electrical energy into usable heat, minimizing waste. The direct heat output ensures that energy goes where it is needed most, which can lower overall consumption. Many far infrared heaters meet energy star certification standards, confirming their efficient performance and environmental benefits.
Pros:
Direct, comfortable warmth with minimal energy loss
Quiet operation with no moving parts
Safe for continuous use in occupied spaces
Suitable for allergy sufferers, as they do not circulate dust
Cons:
Limited range; best for targeted heating zones
Higher initial investment compared to basic heaters
Far infrared heaters offer an efficient and safe solution for those who prioritize comfort and energy savings.
Quartz IR emitters generate heat by passing electricity through a quartz tube containing a heating element. This process produces infrared radiation, which delivers rapid and focused heat output. The technology allows for precise temperature control and quick thermal response, making it ideal for both residential and industrial applications.
Quartz IR emitters from Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology serve a wide range of industries. They support processes such as wafer processing, digital printing, paint drying, glass heating, and plastic molding. The company’s product lineup includes short wave, fast medium wave, and medium wave infrared lamps, as well as carbon infrared heaters. These solutions provide efficient and stable heat distribution, which improves production quality and operational efficiency.
Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology quartz IR emitters hold certifications such as ISO 9000, QC-1, TUV, ATEX, IECEx, and certificates of conformity.
The technology delivers high energy efficiency, rapid thermal response, and precise temperature control.
These emitters help reduce energy consumption and operational costs while supporting process stability.
The products meet strict industry standards for safety and reliability.
Quartz IR emitters achieve impressive efficiency rates, converting up to 96% of electrical energy into usable heat. This high efficiency translates to significant energy savings and lower fuel costs, often reducing energy expenses by 20% to 50% compared to traditional heating methods. Many models carry energy star certification, which assures users of their efficient and environmentally friendly performance.
Pros:
Extremely efficient heat output with rapid response
Certified for safety and reliability
Versatile applications in both home and industry
Reduces operational costs and carbon footprint
Cons:
Requires proper installation for optimal performance
Some models may be specialized for industrial use
Quartz IR emitters from Huai’an Infrared Heating Technology represent a leading choice for those seeking efficient, certified, and high-performance heating solutions.
LED Heating Solutions
LED technology has transformed both lighting and heating applications. Most people know LEDs for their role in energy-efficient lighting, but advancements in led technology have led to new heating solutions. LED-based heating panels use semiconductor materials to produce radiant warmth with minimal energy loss. These systems suit outdoor environments, such as patios and walkways, where efficient and safe heat is essential.
LED heating solutions stand out for their long lifespan and low maintenance. Typical led bulbs last between 25,000 and 35,000 hours, which is far longer than halogen infrared lamps. They consume about 8 watts for comparable brightness, making them highly efficient. LEDs emit only 10-20% of their energy as heat, reducing HVAC loads and improving comfort in both indoor and outdoor spaces.
LED heating panels offer precise temperature control and instant heat, making them ideal for outdoor seating areas and energy-efficient outdoor lighting installations.
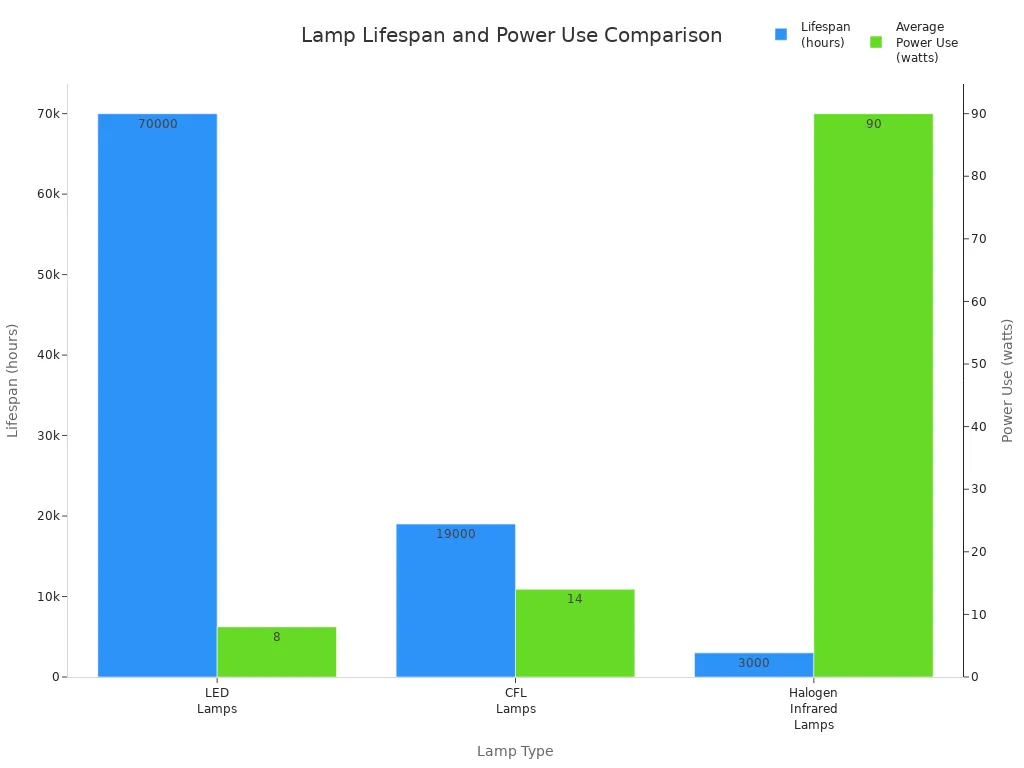
Choosing the right energy-efficient light bulb can significantly impact household and industrial energy consumption. LEDs and cfl bulbs use up to 80% less energy than traditional incandescent or halogen infrared lamps. The following table highlights key differences:
Feature | LED Lamps | CFL Lamps | Halogen Infrared Lamps |
|---|---|---|---|
Lifespan (hours) | 40,000 to 100,000 | 8,000 to 30,000 | 2,000 to 4,000 |
Average Power Use | ~8 watts | ~14 watts | ~90 watts |
Energy Savings | Uses 80-90% less energy than halogen; ~30% less than CFL | More efficient than incandescent; less efficient than LED | Highest energy consumption among the three |
Heat Emission | 10-20% of energy consumed as heat | 30-80% of energy as heat | 80-90% of energy as heat (very hot) |
Additional Notes | Longest lifespan, low heat output reduces HVAC load | Contains mercury, moderate lifespan and efficiency | Short lifespan, high heat output, fire hazard risk |
Energy-efficient bulbs such as LEDs provide long-term cost savings. They last up to 25 times longer than incandescent bulbs, reducing waste and replacement frequency. CFLs, or compact fluorescent light bulbs, offer moderate efficiency and lifespan but require careful recycling due to mercury content. Energy-saving light bulbs also help lower carbon footprints and reduce strain on local power grids.
Tip: Start replacing bulbs in frequently used fixtures to maximize energy savings. Choose bulbs based on lumens and color temperature for optimal lighting quality.
CFL heaters use compact fluorescent light technology to provide both lighting and supplemental heat. While cfl bulbs are more efficient than incandescent options, they do not match the efficiency of led solutions. CFLs typically last 10,000 to 15,000 hours and use about 14 watts for similar brightness. They emit 30-80% of their energy as heat, which can contribute to warming small spaces.
CFL heaters suit indoor environments where moderate heat and efficient lighting are needed. They contain mercury, so users must recycle them properly. Compact fluorescent light bulbs offer a balance between cost and performance, but led alternatives deliver greater efficiency and longer service life.
CFLs provide moderate energy savings compared to halogen infrared lamps.
They work well in enclosed fixtures and small rooms.
Proper disposal is essential due to mercury content.
CFLs offer a lower upfront cost but higher operating costs over time compared to led bulbs.
Energy-efficient outdoor lighting often relies on led technology for superior performance and durability. Outdoor spaces benefit from the instant brightness and low heat output of led fixtures, which also reduce energy consumption.
Heating systems achieve the most energy-efficient option when users match system size to actual needs and adopt advanced controls. Facility managers often collect annualized data to right-size equipment, avoiding oversized systems that waste energy. Lowering hot water temperatures to the minimum required for comfort enables the use of more efficient and commercially available alternatives. Many organizations replace central steam systems with heat pumps or modular electric solutions, which further improve energy savings. Regular reviews of energy conservation measures help align operations with sustainability goals and maximize savings.
Building owners can also optimize distribution systems by insulating pipes and ducts, reducing heat loss. Zoning and variable air volume systems deliver heat only where needed, increasing efficiency. High-efficiency boilers, heat pumps with high COP values, and smart thermostats all contribute to the most energy-efficient option for both homes and businesses. Monitoring performance and adjusting settings ensures systems operate at peak efficiency, supporting ongoing energy savings and lower electricity bills.
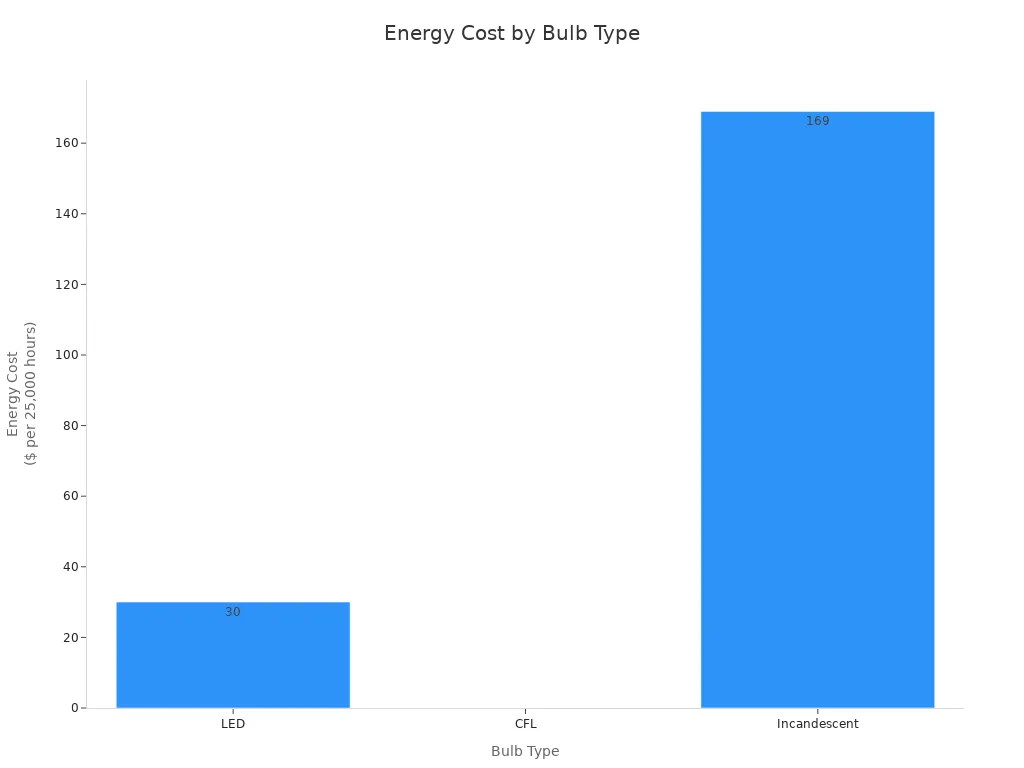
The cost of heating includes purchase, operation, and maintenance. Halogen infrared lamps have a moderate upfront cost but higher operating expenses due to significant energy consumption. LED alternatives, while more expensive initially, offer substantial energy savings over time. For example, LED lamps use up to 80-90% less energy than halogen lamps and last up to 50,000 hours, reducing replacement and maintenance costs. Advanced infrared solutions, such as quartz IR emitters, can cut fuel costs by 20%-50% compared to traditional methods.
The table below summarizes key differences:
Heater Type | Purchase Cost | Operating Cost | Maintenance Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Halogen Infrared Lamps | Moderate (5-8 USD/lamp) | High (electricity) | Low | Shorter lifespan, higher energy consumption, frequent replacements |
LED Lamps | Higher | Low (significant savings) | Very Low | Long lifespan, up to 90% energy savings, eco-friendly |
Moderate to High | Low (20%-50% fuel savings) | Low | High efficiency, industrial and residential use | |
Oil-Filled Radiators | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Steady heat, efficient for continuous use |
Heat Pumps | High | Very Low | Low to Moderate | Most energy-efficient option, long-term savings |
Tip: Investing in the most energy-efficient option may require a higher upfront cost, but the long-term savings on energy and maintenance often outweigh the initial expense.
Switching to efficient alternatives reduces the impact on the environment. LED lamps and advanced infrared heaters lower energy consumption, which leads to fewer carbon emissions. For example, the EU projects that replacing halogen lamps with LED alternatives could save 17 million tons of CO2 by 2025. LED and quartz IR emitters contain no hazardous materials, making them safer for the environment. Oil and gas boilers, in contrast, rely on non-renewable fuels and produce higher emissions.
Efficient heating technologies support a cleaner environment by minimizing waste and reducing the need for frequent replacements. Eco-friendly choices like LED and advanced infrared systems help users achieve both energy savings and environmental goals.
Aspect | Halogen Lamps | LED Lamps |
|---|---|---|
Energy Consumption | High (300-1000 watts) | Low (30-100 watts) |
Energy Savings | N/A | Up to 80-90% less energy used |
Operating Cost | High | Low (significant savings) |
Lifespan | Shorter | Up to 50,000 hours |
Environmental Impact | Higher carbon emissions | Reduced CO2 emissions |
Hazardous Materials | Possible | None |
Choosing the most energy-efficient option not only delivers energy savings but also protects the environment for future generations.
Selecting the right heating solution starts with evaluating the size of the space. Small rooms, such as bedrooms or offices, benefit from compact heaters like ceramic or panel models. These units deliver targeted warmth without wasting energy. For medium-sized areas, oil-filled radiators or far infrared heaters provide steady, even heat. Large spaces, including open-plan living rooms or industrial workshops, require more powerful systems. Heat pumps and quartz IR emitters excel in these environments, offering efficient coverage and consistent temperature control.
Outdoor areas present unique challenges. Patios, decks, and garden seating zones need heaters designed for weather resistance and rapid heat delivery. Quartz IR emitters and specialized outdoor panel heaters ensure comfort even in open-air settings. Energy-efficient outdoor lighting can complement these systems, enhancing both safety and ambiance.
Tip: Measure the square footage of the area before choosing a heater. Manufacturers often list recommended room sizes for each product.
Usage patterns play a critical role in determining the most suitable heating alternative. Different applications—such as industrial heating, medical facilities, or commercial spaces—demand specific features. Industrial environments often require high-intensity, durable solutions. Quartz IR emitters and heat pumps meet these needs with robust performance and precise control. Medical and commercial settings may prioritize uniform heat distribution and safety, making panel heaters or far infrared models ideal.
Industrial heating dominates demand, accounting for about 65% of the market.
Medical and commercial sectors show growth potential with tailored infrared technologies.
Applications needing precise spectral control or high durability often favor advanced infrared solutions.
Environmental regulations and energy consumption concerns influence adoption in each context.
In residential settings, usage patterns vary. Some users need quick, occasional warmth, while others require continuous heating. Portable ceramic heaters suit short-term use, while oil-filled radiators or heat pumps work better for long-term comfort. Outdoor usage, such as heating patios or walkways, calls for weatherproof options with instant heat output.
Budget considerations influence both the initial purchase and long-term operating costs. Halogen lamps offer the lowest upfront price, typically ranging from $1 to $5 per bulb. However, their shorter lifespan and higher energy consumption increase overall expenses. LEDs, while more expensive initially (starting at $1.50 per bulb), last much longer and use less energy, resulting in significant savings over time. CFLs fall between halogen and LED options in both cost and efficiency.
For large-scale installations, such as airport or industrial lighting, the budget range widens. Halogen lamps remain affordable for smaller projects, with individual units costing $20 to $25. LED systems, though more energy-efficient and durable, can cost $800 to $1,300 per lamp, with infrastructure upgrades reaching up to $2 million. These higher costs may be prohibitive for some organizations but deliver long-term energy and maintenance savings.
Note: Investing in efficient heating and lighting solutions often leads to lower utility bills and reduced replacement frequency, offsetting higher initial costs.
Safety stands as a top priority when selecting any heating solution. Users must consider not only the device's built-in safety features but also the broader environment where the heater will operate. Modern heating alternatives often include advanced protections that help prevent accidents and reduce health risks.
Key safety features to prioritize include:
Automatic shut-off: Devices with this feature turn off if they overheat or tip over, reducing fire hazards.
Cool-to-touch surfaces: Heaters with insulated exteriors help prevent burns, especially in homes with children or pets.
Overheat protection: This function monitors internal temperatures and shuts down the unit if it gets too hot.
Stable design: A wide base or wall-mounting option prevents accidental tipping.
Child lock controls: These settings restrict unauthorized adjustments, adding an extra layer of safety.
In industrial and commercial settings, safety protocols extend beyond the heater itself. Facility managers should implement hydration protocols, work/rest schedules, and provide access to shade or cooling stations. Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as cooling vests and bandanas can help workers avoid heat stress during prolonged exposure. Research shows that these cooling PPE alternatives effectively reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses.
Tip: Education and training play a critical role in safety. Workers and residents should learn to recognize symptoms of heat-related illnesses and know how to respond quickly.
Access to drinking water with electrolytes further lowers the risk of acute kidney injury, especially in high-heat environments. Modern facilities often include air-conditioned trailers or portable shelters as part of comprehensive safety measures.
When evaluating heating alternatives, users should look for products with recognized safety certifications. Brands that offer certified heaters, such as those with TUV or other international safety marks, provide added peace of mind. Certified products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet strict safety standards.
Choosing the right heating solution involves more than just energy efficiency or cost. Safety features and protocols protect both people and property, making them essential considerations for any home or workplace.
Choosing the right alternative to halogen infrared lamps ensures safer, cleaner warmth for any space. Top options like ceramic heaters, oil-filled radiators, panel heaters, heat pumps, far infrared heaters, and quartz IR emitters deliver reliable performance and environmental benefits. Industry experts recommend several best practices:
Select energy-efficient systems such as heat pumps.
Use smart or programmable thermostats for optimal control.
Seal and insulate homes to prevent energy loss.
Schedule regular maintenance and replace filters.
Hire qualified contractors for installation and repairs.
Prioritizing energy savings and safety helps users achieve comfort while reducing costs. Trusted brands and certified products offer added peace of mind.
Energy-efficient alternatives operate at lower surface temperatures and often include safety features like automatic shut-off and cool-to-touch exteriors. These features reduce the risk of burns and fire hazards, making them safer for heating spaces in homes and workplaces.
Energy-efficient bulbs, such as led and compact fluorescent light options, use less energy to produce the same brightness as traditional bulbs. This lower energy consumption results in significant energy savings and helps reduce electricity bills over time.
Advancements in led technology have produced led panels and fixtures designed for outdoor environments. These products provide efficient heat output and reliable performance, making them ideal for patios, walkways, and other outdoor areas that require energy-efficient outdoor lighting and warmth.
Quartz IR emitters and heat pumps stand out as the most energy-efficient option for large industrial heating spaces. These systems deliver high efficiency, rapid heat output, and can achieve energy star certification, supporting both operational savings and a cleaner environment.
Switching to energy-efficient lighting, such as energy-saving light bulbs and led fixtures, reduces energy consumption and lowers carbon emissions. These eco-friendly solutions help protect the environment by minimizing waste and supporting sustainability goals.
Cfl bulbs, or compact fluorescent light bulbs, provide efficient lighting and emit moderate heat output. While not as efficient as led for heating, they offer a balance between cost and performance for small indoor spaces.
Energy star certification ensures that products meet strict efficiency and safety standards. Certified heaters and energy-efficient light bulb options deliver reliable performance, lower energy consumption, and contribute to energy savings and a healthier environment.
Users should select the right size heater, use programmable thermostats, and maintain equipment regularly. These steps, combined with energy-efficient options, help maximize efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and achieve lower electricity bills.

